110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

携带 APOE ε4 等位基因等位基因的阿尔茨海默病患者的 STARD6 和近 ECHDC3 基因多态性的关联分析
Authors Yin J, Feng W, Yuan H, Yuan J, Wu Y, Liu X, Jin C, Cheng Z
Received 6 September 2018
Accepted for publication 14 December 2018
Published 11 January 2019 Volume 2019:15 Pages 213—218
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S186705
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yu-Ping Ning
Background and purpose: Lipid
metabolism plays an important role in Alzheimer’s disease (AD), and recent
evidence suggests that single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in the
StAR-related lipid transfer domain 6 (STARD6 ) and near the enzyme enoyl CoA hydratase domain
containing 3 (ECHDC3 )
gene are related to plasma lipid levels or lipid traits in AD.
Materials and methods: To
identify whether the variants in or near the STARD6 and ECHDC3 genes
contribute to AD susceptibility, we carried out an association analysis
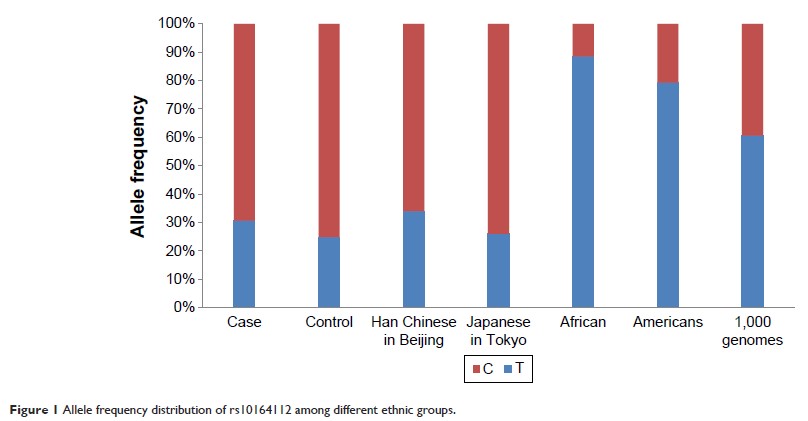
of STARD6 rs10164112
and ECHDC3 rs7920721
in combination with the apolipoprotein E (APOE ) ε4 allele in a case–control study (278 cases,
509 controls) in China.
Results: We
identified that SNP rs10164112 in the STARD6 gene was a risk factor associated with AD
and the APOE ε4
carriers (all P <0.05) after Bonferroni correction. However,
multivariate logistic regression analysis indicated that only the minor T
allele of STARD6 rs10164112
combined with the APOE ε4 allele increased the risk of AD under the
additive and dominant models (additive model: P =0.0078, OR=1.988,
95 % CI: 1.198–3.298; dominant model: P =0.0172, OR=2.169, 95% CI: 1.147–4.102).
Conclusion: These
results suggest that the rs10164112-T allele is not an independent risk factor
for AD patients. However, in combination with the APOE ε4
allele, the rs10164112-T allele has been found to be a risk factor for AD in
the Han Chinese population reported in this study.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s
disease, STARD6 , ECHDC3 , APOE , polymorphism,
association study