110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

2 型糖尿病会增加慢性乙型肝炎病毒感染者患肝细胞癌的风险:汇总分析和系统回顾
Authors Tan Y, Wei S, Zhang W, Yang J, Yang J, Yan L
Received 20 September 2018
Accepted for publication 21 December 2018
Published 14 January 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 705—713
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S188238
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Rituraj Purohit
Background: Type 2 diabetes
mellitus has been proved to be a risk factor of hepatocellular carcinoma, but
how diabetes affects incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma among patients with
chronic hepatitis B virus infection remains controversial.
Methods: A comprehensive
search of Medline and Embase was performed. Incidence of hepatocellular
carcinoma in chronic hepatitis B patients was the primary outcome. Pooled HRs
and 95% CIs were calculated to assess the correlation between diabetes and
incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma.
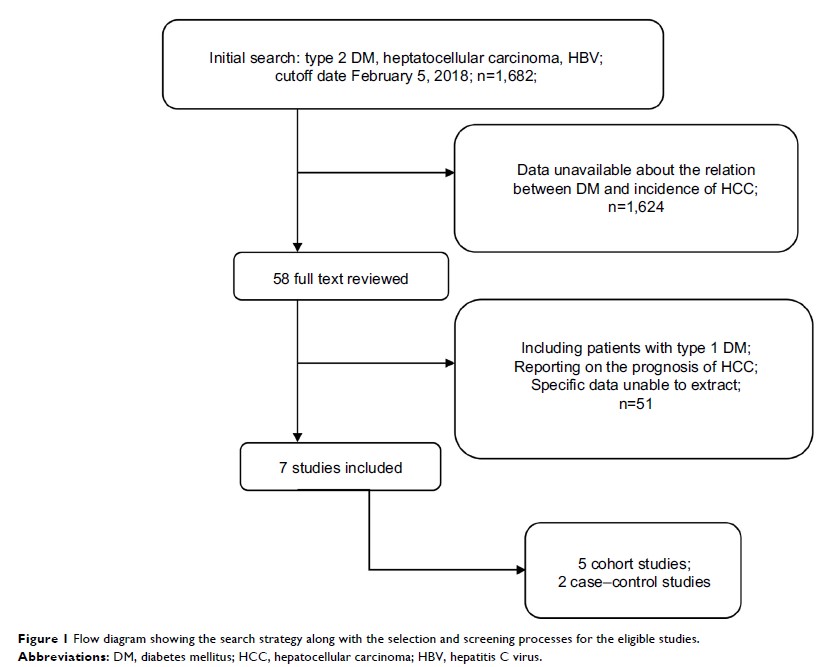
Results: Five cohort
studies and two case–control studies were identified, with a total of 21,842
chronic hepatitis B patients. The diabetes mellitus cohort was found to have
increased incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma (pooled HR 1.77, 95% CI
1.28–2.47; fixed effect) and worse overall mortality (pooled RR 1.93, 95% CI
1.64–2.27; fixed effect) in comparison with those without diabetes. In
case–control studies, hepatocellular carcinoma cases were found to have an
insignificantly elevated diabetes mellitus rate in comparison with the control
group.
Conclusion: Type 2 diabetes
mellitus is significantly associated with increased risk of hepatocellular
carcinoma among patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection, and
aggressive management of diabetes mellitus is strongly suggested.
Keywords: type 2 diabetes
mellitus, hepatocellular carcinoma risk, HBV-infected