110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

通过 S-指数建立的样本模型可预测原发性肝细胞癌根治性切除后的总体存活率
Authors Chen L, Cai BB, Zhou CJ, Hou XQ, Hu SP, Fang G, Chen WC, Li LH, Yang WJ
Received 6 November 2018
Accepted for publication 7 December 2018
Published 14 January 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 693—703
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S193593
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Kenan Onel
Purpose: Prognostic
prediction after curative resection of primary hepatocellular carcinoma (PHCC)
remains an arduous task. The S-index calculated from γ-glutamyl transpeptidase,
albumin, and platelets is reported to predict the severity of liver fibrosis.
We constructed a nomogram for predicting the survival probability of PHCC based
on a new indicator, the S-index, combined with other routine clinical
parameters.
Patients and methods: We
selected 490 patients with PHCC postradical surgery at the First Affiliated
Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University between January 2007 and January 2014.
The subjects were randomly allocated into the training cohort and the
validation cohort in the ratio 7:3 by the digital method. Important variables
screened by univariate analysis were included in multivariate analysis to
obtain independent risk factors for predicting the prognosis of PHCC. The
construction of the nomogram was based on Cox proportional hazard regression
models. The concordance index (C-index) was used in the nomogram for evaluating
the model performance for prognosis. We drew time-dependent receiver operating
characteristic curves to compare our model with other staging systems.
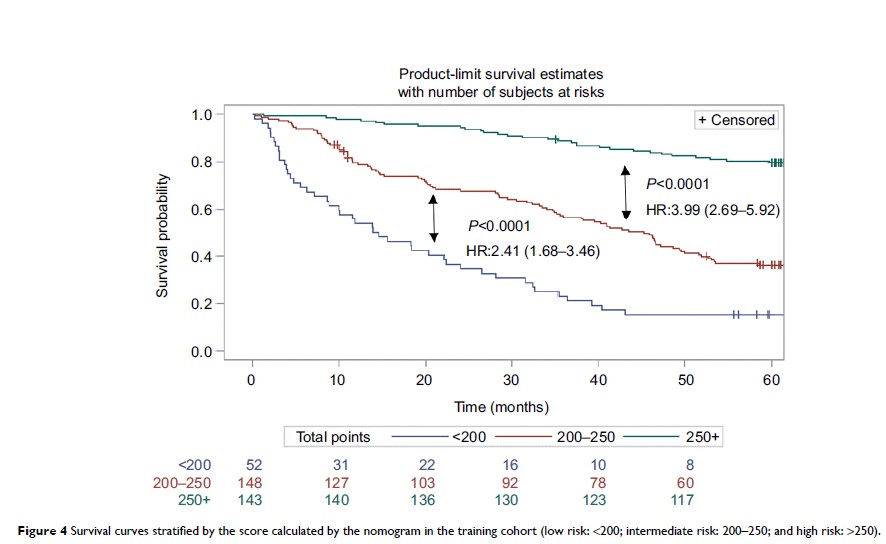
Results: The
nomogram based on six independent risk factors after multivariate analyses had
good predictive power after radical surgery of PHCC. In the training and
validation groups, the C-index of the nomogram was highly consistent for
evaluating survival from PHCC. Compared with the traditional scoring system,
the areas under time-dependent receiver operating characteristic curves were
0.7382, 0.7293, and 0.7520 for 1-, 3-, and 5-year overall survival, respectively.
In summary, the nomogram showed excellent results in terms of prognosis of
PHCC.
Conclusion: Based on
the S-index and the other clinical indicators, we developed a precise nomogram
that predicts the survival probability of patients with PHCC after radical
surgery. This tool can provide effective information for surgeons and patients.
Keywords: PHCC,
radical resection, nomogram, prognosis