110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

YB-1 通过激活 MDM2/p53 通路调节胶质瘤细胞的耐药性
Authors Tong H, Zhao K, Zhang J, Zhu J, Xiao J
Received 28 August 2018
Accepted for publication 22 November 2018
Published 14 January 2019 Volume 2019:13 Pages 317—326
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S185514
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Qiongyu Guo
Background: Y-box-binding
protein-1 (YB-1) is aberrantly expressed in a variety of cancers. However, the
biological functional role of YB-1 in glioma is not yet clear.
Methods: The
expression of MDM2 and YB-1 was analyzed by real time PCR. Overexpression and
knockdown of YB-1 in glioma cells were created by transfection of pcDNA-YB-1
and siRNA against YB-1, respectively. Cell viability was performed by CCK8
assay.
Results: Our
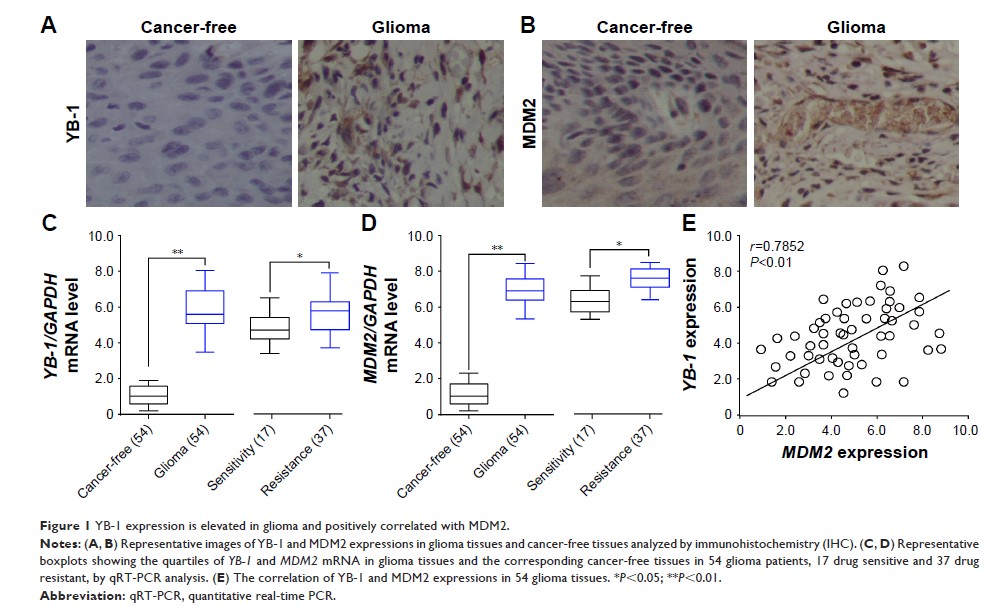
findings showed that glioma tissues had higher expressions of YB-1 than that in
cancer-free tissues in 54 glioma patients, which were also positively
correlated with Murine MDM2 expression. Overexpression of YB-1 or MDM2 renders
a drug resistance feature in glioma cell exposed to temozolomide (TMZ), by
directly targeting p53. Genetic or chemical inhibition of MDM2 significantly
blocked YB-1-modulated response of glioma cells to TMZ. Moreover, inhibition of
YB-1 or MDM2 reduced glioma cells metastasis and mortality in mice.
Conclusion: YB-1
facilitates the resistance of glioma cells to TMZ by direct activation of
MDM2/p53 signaling and represents a promising molecular target for glioma
treatment.
Keywords: glioma,
p53, Murine double minute 2, Y-box binding protein-1, drug resistance,
temozolomide