110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

由地塞米松 - 肽结合物形成的高载药纳米颗粒,用于治疗兔内毒素诱导的葡萄膜炎
Authors Yu X, Zhang R, Lei L, Song Q, Li X
Received 4 July 2018
Accepted for publication 29 November 2018
Published 14 January 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 591—603
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S179118
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Purpose: To
develop and demonstrate the effectiveness of a novel dexamethasone (Dex)
nanoformulation for treating uveitis.
Materials and methods: We designed and
screened a dexamethasone-peptide conjugate (Dex-SA-FFFE), formed via a
biodegradable ester bond linkage, that could spontaneously form high drug
payload nanoparticles in aqueous solution for treating uveitis.
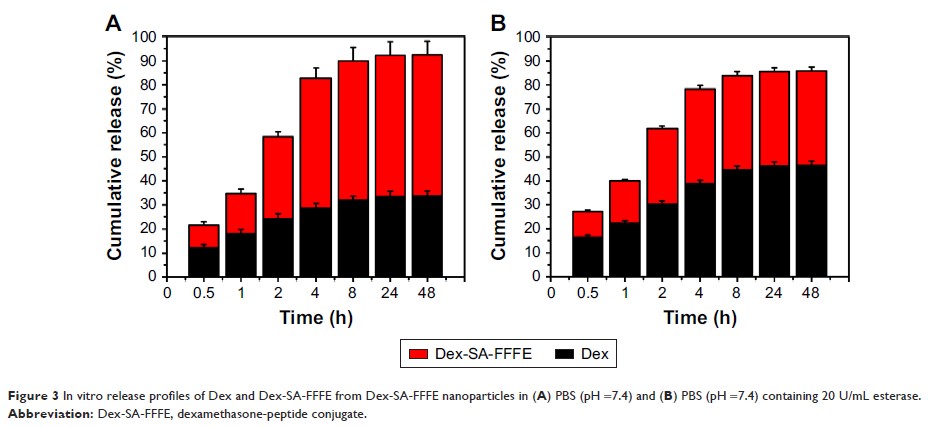
Results: An in vitro
release study indicated that Dex and Dex-SA-FFFE sustainably released from
Dex-SA-FFFE nanoparticles over a 48 h study period. Meanwhile, the formed
Dex-SA-FFFE nanoparticles hardly caused cytotoxicity in human corneal
epithelial cell at drug concentrations up to 1 mM after 24 h of incubation but
reduced cell viability after 48 h and 72 h of incubation. An in vitro
anti-inflammatory efficacy assay showed that the Dex-SA-FFFE nanoparticles
exhibited a comparable anti-inflammatory efficacy to that of Dex in
lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-activated RAW264.7 macrophages via significant
decreases in the secretion of various pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., nitric
oxide, tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-6). Topical instillation of
Dex-SA-FFFE nanoparticles showed good ocular tolerance without causing changes
in corneal thickness and intraocular pressure during the entire study period.
Furthermore, topical instillation of Dex-SA-FFFE nanoparticles displayed a
comparable in vivo therapeutic efficacy to that of dexamethasone sodium
phosphate (Dexp) aqueous solutions in an endotoxin-induced uveitis (EIU) rabbit
model.
Conclusion: Based on these
results, it is reasonable to believe that the proposed Dex-SA-FFFE
nanoparticles might have great application for the treatment of anterior
uveitis.
Keywords: drug-peptide
conjugate, self-assembly, ocular inflammation, in vivo, nanoparticle