110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

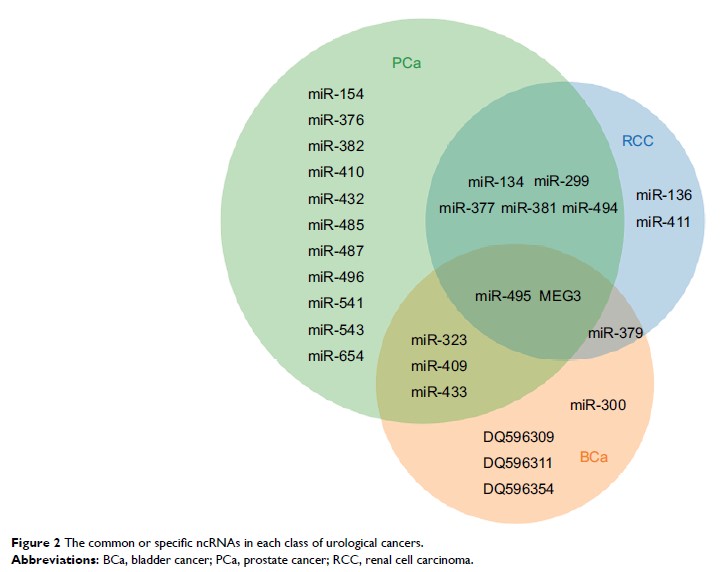
位于 DLK1-DIO3 印记域的 ncRNA 失调:在泌尿系肿瘤中的作用
Authors Li J, Shen H, Xie H, Ying Y, Jin K, Yan H, Wang S, Xu M, Wang X, Xu X, Xie L
Received 13 October 2018
Accepted for publication 6 December 2018
Published 15 January 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 777—787
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S190764
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Chien-Feng Li
Abstract: Genomic
imprinting has been found to be involved in human physical development and
several diseases. The DLK1-DIO3 imprinted domain is located on human
chromosome 14 and contains paternally expressed protein-coding genes (DLK1 , RTL1 , DIO3 ) and numerous
maternally expressed ncRNA genes (MEG3 , MEG8 , antisense RTL1 , miRNAs, piRNAs, and snoRNAs). Emerging
evidence has implicated that dysregulation of the DLK1-DIO3 imprinted
domain especially the imprinted ncRNAs is critical for tumor progressions.
Multiple miRNAs and lncRNAs have been investigated in urological cancers, of
which several are transcribed from this domain. In this review, we present
current data about the associated miRNAs, lncRNAs, and piRNAs and the
regulation of differentially methylated regions methylation status in the
progression of urological cancers and preliminarily propose certain concepts
about the potential regulatory networks involved in DLK1-DIO3 imprinted
domain.
Keywords: ncRNAs, DLK1-DIO3 imprinted
domain, epigenetics, regulatory network, urological cancers, DMRs , MEG3