110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

miR-4262 的低水平可预测不良预后并靶向原癌基因 CD163 以抑制胃癌细胞增殖和侵袭
Authors Zhang H, Jiang H, Zhang H, Liu J, Hu X, Chen L
Received 17 September 2018
Accepted for publication 16 December 2018
Published 15 January 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 599—607
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S187881
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Jianmin Xu
Background: miR-4262
was identified as a tumor promoter in several cancers, but its exact role in
gastric carcinoma is still largely unknown.
Methods: The
expression of miR-4262 was detected in gastric cancer tissues. Different
concentrations of miR-4262 mimic and miR-4262 antagomir were respectively
transfected into primary gastric carcinoma cells. After incubation for 72 h,
the overexpression efficiencies were confirmed by qPCR, cell proliferation was
detected with the CCK-8 assay, cell apoptosis was detected by using the
PI/Annexin V Cell Apoptosis Kit, and cell invasion was detected with the
Transwell invasion assay. The molecular mechanisms underlying the action of
miR-4262 in gastric carcinoma cells were also explored.
Results: In this
study, we found that miR-4262 was significantly downregulated in gastric tissue
from gastric cancer patients compared with that from the control group.
Moreover, the level of miR-4262 was significantly lower in advanced gastric
carcinoma. Additionally, lower level of miR-4262 was correlated with poorer prognosis
and lower survival rate in gastric cancer patients. Then, different
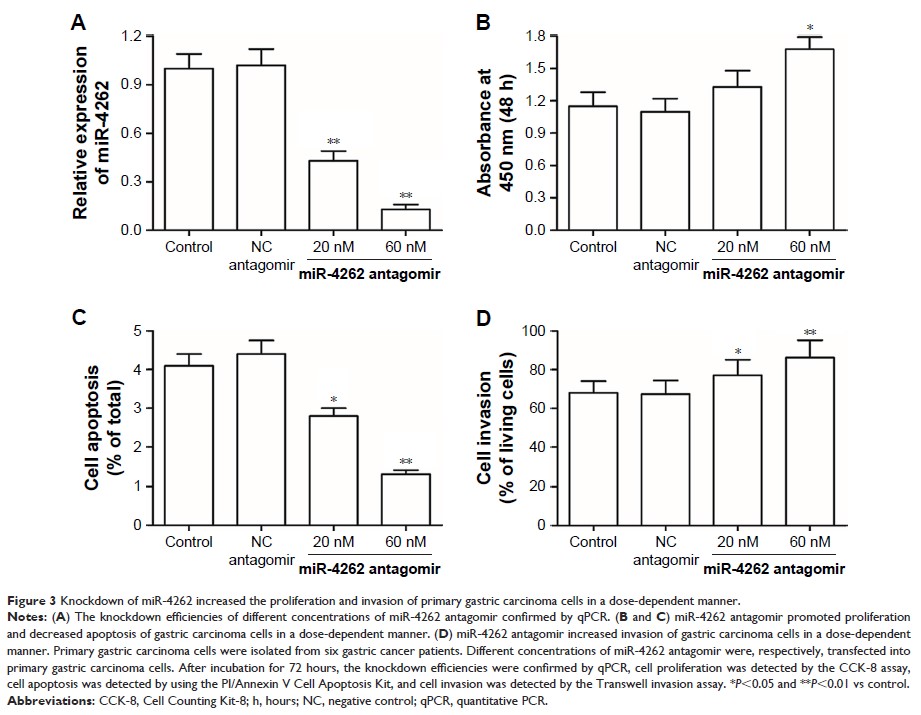
concentrations of miR-4262 mimic and miR-4262 antagomir were transfected into
primary gastric carcinoma cells, respectively. The results showed that miR-4262
mimic suppressed proliferation and invasion and promoted cell apoptosis in a
dose-dependent manner in gastric carcinoma cells. In contrast, miR-4262
antagomir increased proliferation and invasion and decreased cell apoptosis in
a dose-dependent manner in gastric carcinoma cells. Furthermore, miR-4262 could
directly target and suppress the expression of the proto-oncogene CD163.
Conclusion: Our
findings indicate that lower level of miR-4262 predicts poorer prognosis in
gastric patients, and miR-4262 can target proto-oncogene CD163 to suppress
gastric cancer cell proliferation and invasion.
Keywords: miR-4262,
gastric carcinoma, prognosis, proliferation and invasion, CD163