110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

包覆阿托伐他汀钙和姜黄素并靶向功能失调的内皮细胞的脂质体在减少动脉粥样硬化中的协同作用
Authors Li X, Xiao H, Lin C, Sun W, Wu T, Wang J, Chen B, Chen X, Cheng D
Received 6 October 2018
Accepted for publication 10 December 2018
Published 15 January 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 649—665
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S189819
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Alexander Kharlamov
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Mian Wang
Background: Atherosclerosis
is a major cardiovascular disease that causes ischemia of the heart, brain, or
extremities, and can lead to infarction. The hypolipidemic agent atorvastatin
calcium (Ato) alleviates atherosclerosis by reducing plasma lipid and
inflammatory factors. However, the low bioavailability of Ato limits its
widespread use and clinical effectiveness. Curcumin (Cur), a natural polyphenol
with antioxidation and anti-inflammation bioactivities, has potential
anti-atherosclerosis activity and may reduce Ato-induced cytotoxicity.
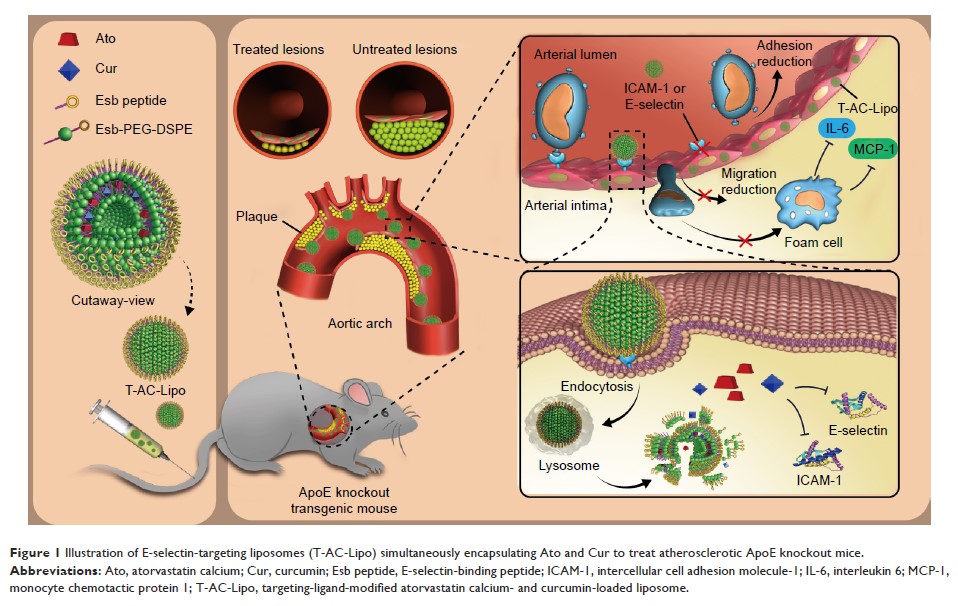
Materials and methods: Liposomes
modified using a targeting ligand (E-selectin-binding peptide) were prepared to
co-deliver Ato and Cur to dysfunctional endothelial cells (ECs) overexpressing
E-selectin. Molecules involved in the inhibition of adhesion (E-selectin and
intercellular cell adhesion molecule-1 [ICAM-1]) and inflammation (IL-6 and
monocyte chemotactic protein 1 [MCP-1]) in human aortic endothelial cells were
evaluated using real-time quantitative PCR, flow cytometry, and
immunofluorescence staining. The antiatherosclerosis effects of liposomes
co-loaded with Ato and Cur in vivo were evaluated using ApoE knockout
(ApoE-/-) mice.
Results: Targeted
liposomes delivered Ato and Cur to dysfunctional ECs, resulting in synergistic
suppression of adhesion molecules (E-selectin and ICAM-1) and plasma lipid
levels. Moreover, this treatment reduced foam cell formation and the secretion
of inflammatory factors (IL-6 and MCP-1) by blocking monocyte migration into
the intima. In addition, Cur successfully reduced Ato-inducible cytotoxicity.
Conclusion: Both
in vitro and in vivo experiments demonstrated that cell-targeted
co-delivery of Ato and Cur to dysfunctional ECs drastically reduces
atherosclerotic lesions with fewer side effects than either Ato or Cur alone.
Keywords: combined
therapy, atorvastatin calcium, curcumin, antiatherosclerosis, targeted
codelivery