110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

系统性免疫炎症指数,乳腺成像报告的超声分型和数据系统用于预测三阴性乳腺癌的疗效
Authors Wang P, Yue W, Li W, Luo Y, Li Z, Shao Y, He Z
Received 30 August 2018
Accepted for publication 13 November 2018
Published 17 January 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 813—819
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S185890
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Kenan Onel
Introduction: This
research was conducted to explore the relationship between the systemic
immune-inflammation index (SII) and breast imaging-reporting and data system
(BI-RADS) classification using ultrasonography and the survival of patients
with triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) in a cohort of Chinese.
Methods: A total
of 215 TNBC patients treated at our hospital between November 2008 and March
2016 were enrolled in this study. We used the log-rank test and Kaplan–Meier
curves to assess the overall survival (OS) and disease-free survival (DFS)
differences between groups. The prognostic role of SII and other
clinicopathological characteristics in TNBC patients were identified using the
Cox regression model.
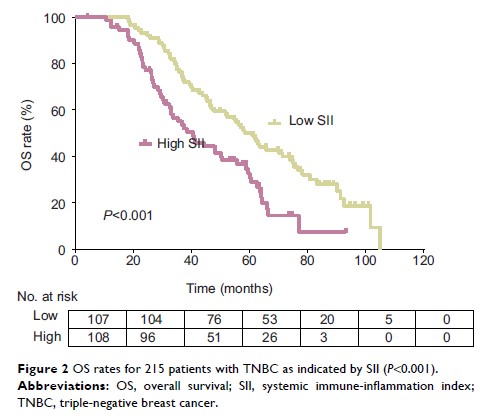
Results: Patients
with low and high SII had median OS of 60.9 and 40.3 months, respectively,
(HR=3.78, 95% CI: 2.16–4.15, P <0.001); while the median DFS was 22.4 months and
14.4 months for TNBC patients with low and high SII, respectively (HR =3.16,
95% CI: 1.82–4.02, P <0.001). For patients with grade 5
ultrasonographic BI-RADS classification, the median DFS and OS were 41.2 and
16.5 months, respectively, whereas, it was 57.7 and 21.3 months, respectively,
for those with BI-RADS grades 3–4 (P <0.01). According to multivariable analyses,
increased SII was a risk factor that independently predicted poor OS (HR =2.96,
95% CI: 2.18–3.98, P <0.001) and DFS (HR = 2.85, 95% CI:
1.62–3.81, P =0.005).
In addition, tumor stage, BI-RADS, and histological grade also independently
predicted poor OS (P =0.002, <0.001, 0.004).
Conclusion: Pretreatment
SII and BI-RADS 5 were independent indicators for prognosis in TNBC patients.
It is imperative to conduct prospective studies to evaluate the potential role
of SII in patient selection, treatment guidance, and design of clinical trials.
Keywords: TNBC,
SII, inflammation, prognosis, immunity