110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

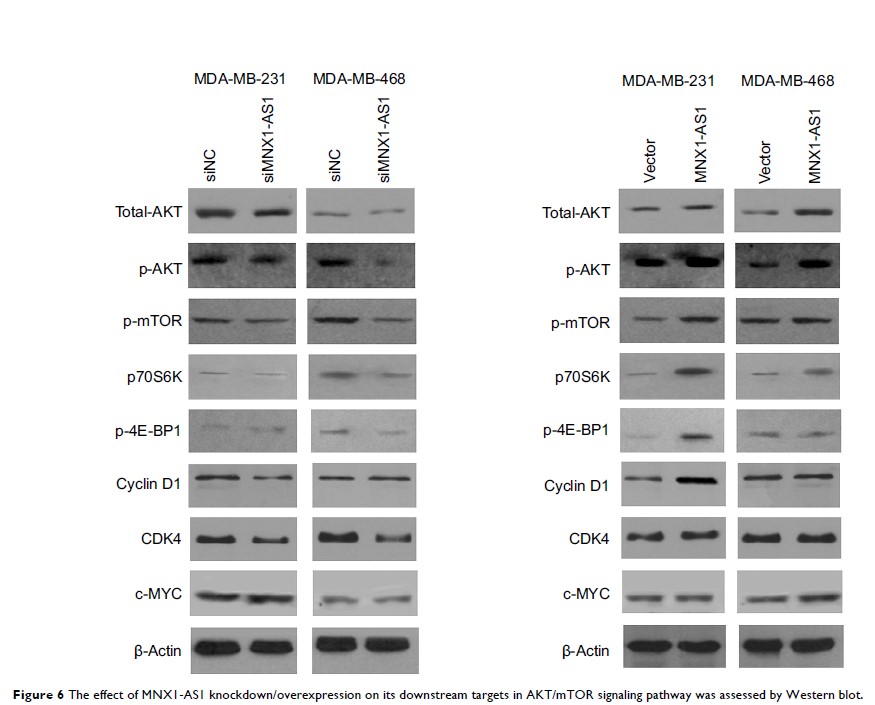
MNX1-AS1 是一种功能性致癌基因,可诱导 EMT 并激活乳腺癌中的 AKT/mTOR 通路和 MNX1
Authors Cheng Y, Pan Y, Pan Y, Wang O
Received 18 September 2018
Accepted for publication 16 December 2018
Published 17 January 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 803—812
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S188007
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Nakshatri
Purpose: lncRNAs
have recently been identified as key regulators of basic biological processes
as well as the pathogenesis of various diseases. Previous studies have shown
that lncRNA MNX1-AS1 promotes cell migration and invasion in ovarian cancer;
however, its role in regulating breast cancer-associated biological processes
remains unclear.
Materials and methods: We
obtained paired specimens of breast cancer tissues and adjacent normal tissues
by modified radical mastectomy from 36 patients, in addition to four breast
cancer cell lines (MDA-MB-231, MDA-MB-468, BT-549 and MCF-7). RNA was isolated
from these tissues and cell lines and subsequently subjected to quantitative
real-time polymerase chain reaction. This was followed by bisulfite deep
sequencing. The cells were also transfected with siRNA against MNX1-AS1. The
cells were then subject to cell proliferation, Transwell migration and invasion
assays. Finally, Western blotting analysis was conducted to determine
expression levels of MNX1, 5-cadherin, Snail and Slug.
Results: Our
results show that MNX1-AS1 expression was significantly higher in breast cancer
tissues than adjacent normal tissues. Moreover, knockdown/overexpression of
MNX1-AS1 inhibits/promotes proliferation, migration and invasion of breast
cancer cells. MNX1-AS1 and its natural sense transcript MNX1 are expressed
synergistically in breast tumor tissues. Our results suggest that MNX1-AS1 is a
functional oncogene that induces epithelial–mesenchymal transition, in addition
to activating AKT/mTOR pathway and its natural sense transcript MNX1 in breast
cancer cells.
Conclusion: Our data
indicate that MNX1-AS1 can serve as a novel therapeutic target in breast
cancer.
Keywords: MNX1-AS1,
breast cancer, oncogene, MNX1, EMT, AKT/mTOR signaling pathway