110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

DRGs 中 GABAergic 调节对颈部切口痛大鼠电针镇痛起到的作用
Authors Qiao LN, Yang YS, Liu JL, Zhu J, Tan LH, Shi YN, Zhu B, Rong PJ
Received 1 August 2018
Accepted for publication 27 November 2018
Published 17 January 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 405—416
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S180165
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Katherine Hanlon
Purpose: Acupuncture therapy is effective for
relieving postoperative pain. Our previous study showed that electroacupuncture
(EA) at Futu (LI18) and Hegu (LI4)–Neiguan (PC6) could alleviate incisional
neck pain, which was related with its effect in upregulating γ-aminobutyric
acid (GABA) expression in cervical (C3–6) dorsal root ganglions (DRGs); but
whether its receptor subsets GABAAA2R and GABABR1 in C3–6 DRGs are involved in EA analgesia or not,
it remains unknown.
Materials and methods: Seventy-five male Sprague Dawley rats were randomized to normal
control, model, LI18, LI4–PC6, and Zusanli (ST36)–Yanglingquan (GB34) groups.
The incisional neck pain model was established by making a longitudinal
incision along the midline of the rats’ neck, followed by repeated mechanical
stimulation. EA was applied to bilateral LI18, LI4–PC6, or ST36–GB34 for 30
minutes at 4, 24, and 48 hours after operation. The thermal pain threshold of
the neck was detected by a tail-flick unit, and the C3–6 DRGs were removed for
assaying the immunoactivity of substance P (SP), GABAAα2R, glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP; a marker
of satellite glial cells [SGCs]), and GABABR1 and the
expression of GABAAα2R and GABABR1 mRNA and proteins using immunofluorescence,
real-time PCR, and Western blotting, respectively.
Results: The
cervical thermal pain threshold was significantly lower in the model group than
the normal group (P <0.001), indicating hyperalgesia after neck
incision, and was considerably increased in both EA-LI18 and LI4–PC6 groups (P <0.001), but
not in ST36–GB34 group compared with model group (P >0.05).
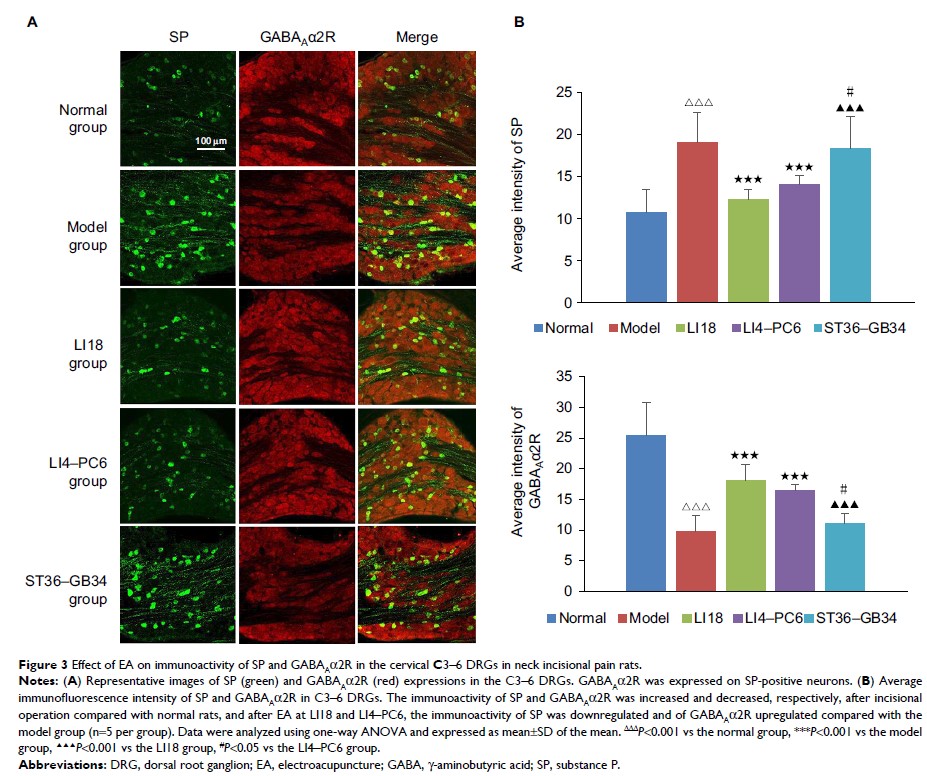
Immunofluorescence staining showed that GABAAα2R R
expressed on SP+ neurons, and GABABR1 on SGCs. EA of LI18 and LI4–PC6 markedly
suppressed the modeling-induced upregulation of the immunoactivity of SP (P <0.001
and P <0.01, respectively)
and GFAP (P <0.01
and P <0.001,
respectively) and significantly reversed neck incision–induced
downregulation of the expression of GABAAα2R and GABABR1 mRNAs and proteins (P <0.05).
Conclusion: EA
of LI18 and LI4–PC6 has an analgesic effect in incisional neck pain rats, which
is related to its effects in upregulating GABAergic inhibitory modulation on
nociceptive peptidergic neurons and SGCs in cervical DRGs.
Keywords: electroacupuncture,
incisional neck pain, substance P, satellite glial cells, GABAAα2R, GABABR1