110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

lncRNA ZEB2-AS1 在胃癌中得到上调,并通过 miR-143-5p/HIF-1α 轴影响细胞增殖和侵袭
Authors Wu F, Gao H, Liu K, Gao B, Ren H, Li Z, Liu F
Received 28 May 2018
Accepted for publication 23 November 2018
Published 18 January 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 657—667
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S175521
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr William Cho
Background: Growing
evidence has implicated the important role of the long non-coding RNAs
(lncRNAs) in gastric cancer progression. In this study, we examined the
expression of lncRNA zinc finger E-box-binding homeobox 2 antisense RNA 1
(ZEB2-AS1) in gastric cancer tissues and elucidated the molecular mechanisms
underlying ZEB2-AS1-mediated gastric cancer progression.
Methods: Quantitative
real-time PCR measured the gene expression level; CCK-8, colony formation and
cell invasion assays determined gastric cancer cell proliferation, growth and
invasion, respectively; the xenograft nude mice model was used to determine in
vivo tumor growth; Bioinformatics analysis and luciferase reporter assay
determined the downstream targets of ZEB2-AS1 and miR-143-5p. The expression of
ZEB2-AS1 was upregulated in gastric cancer cell lines.
Results: Knockdown
of ZEB2-AS1 suppressed gastric cancer cell proliferation, growth and invasion,
and also suppressed in vivo tumor growth in the nude mice. Overexpression of
ZEB2-AS1 potentiated gastric cancer cell proliferation, growth and invasion.
Bioinformatics analysis and luciferase reporter assay showed that miR-143-5p
was a direct target of ZEB2-AS1 and was negatively regulated by ZEB2-AS1.
Furthermore, hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) was found to be a target of
miR-143-5p and was negatively regulated by miR-143-5p. The rescue in vitro
assays showed that the effects of ZEB2-AS1 overexpression on gastric cancer
cell proliferation, growth and invasion was mediated via miR-143-5p/HIF-1α.
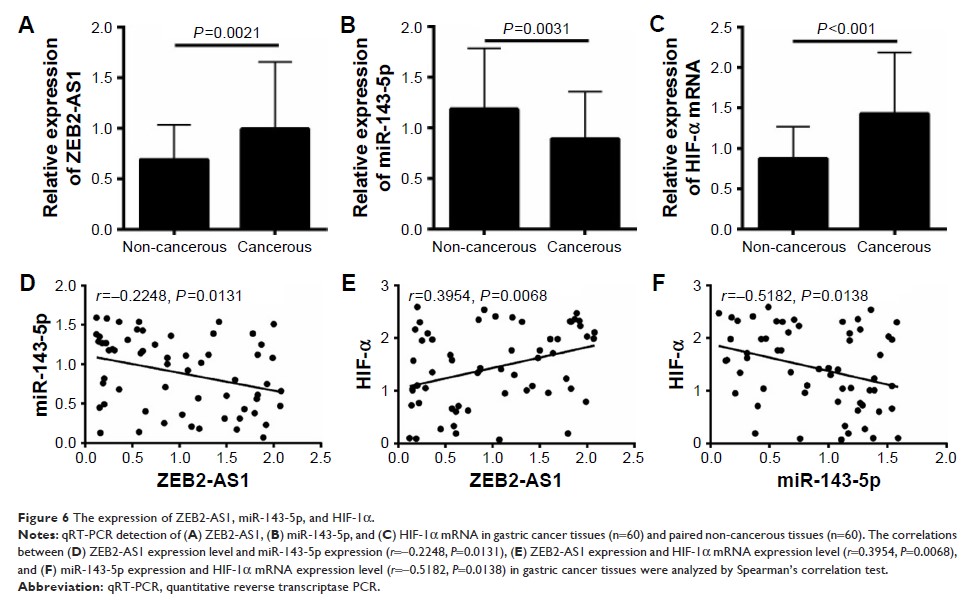
ZEB2-AS1 and HIF-1α was upregulated in gastric cancer tissues, while miR-143-5p
was down-regulated; and ZEB2-AS1 expression level was inversely correlated with
miR-143-5p expression level, and positively correlated with HIF-1α mRNA
expression level; while miR-143-5p expression level was inversely correlated
with HIF-1α expression level. High ZEB2-AS1 expression level was correlated
with poor differentiation, lymph node metastasis and distant metastasis.
Conclusion: Collectively,
our results indicated that ZEB2-AS1 was up-regulated in gastric cancer tissues
and cells and promoted cell proliferation and metastasis through
miR-143-5p/HIF-1α pathway, which may provide a promising target for treatment
of gastric cancer.
Keywords: gastric
cancer, ZEB2-AS1, miR-143-5p, HIF-1α, cell proliferation, metastasis