110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

LncRNA SNHG16 通过调节 miR-497 驱使乳头状甲状腺癌的增殖和侵袭
Authors Wen Q, Zhao L, Wang T, Lv N, Cheng X, Zhang G, Bai L
Received 8 September 2018
Accepted for publication 13 December 2018
Published 18 January 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 699—708
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S186923
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Manfred Beleut
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Federico Perche
Background: Long
noncoding small nucleolar RNA host gene 16 (SNHG16) has been shown to play an
oncogenic role in multiple cancers. However, the biological roles and mechanism
of SNHG16 action in the regulation of papillary thyroid cancer (PTC) remains
unknown. The aims of this study were to investigate the roles and the possible
mechanism of SNHG16 in PTC progression.
Materials and methods: The
expression of SNHG16 PTC tissues and cell lines was detected by
reverse-transcription quantitative PCR (qRT-PCR). The effect of SNHG16 on cell
proliferation, apoptosis, migration, and invasion was detected by Cell Counting
Kit-8, flow cytometry, wound-healing assay, and Matrigel invasion assay,
respectively. In addition, the regulatory relationships between SNHG16 and
miR-497 were explored by luciferase reporter assay and qRT-PCR.
Results: The
SNHG16 expression was upregulated in PTC tissues and cell lines, whose
expression was positively associated with advanced TNM stage and lymph node
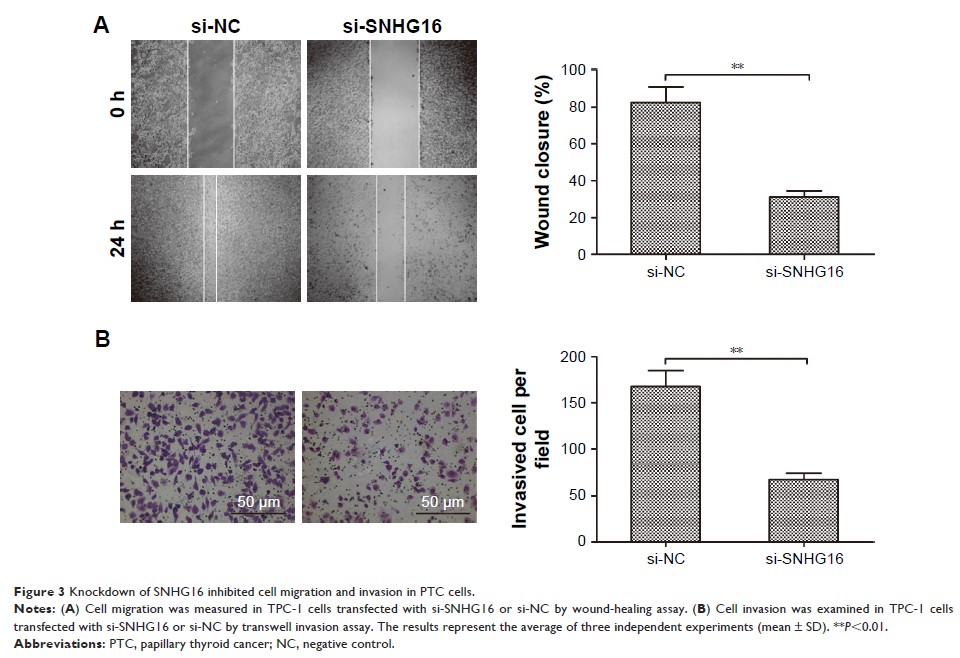
metastasis. Function analysis demonstrated that depletion of SNHG16 in PTC
cells significantly inhibited cell proliferation, induced cell apoptosis, and
suppressed cell migration and invasion abilities. Mechanistic studies indicated
that SNHG16 functioned as an endogenous sponge for miR-497 to regulate its
target genes brain-derived neurotrophic factor and yes-associated protein 1
expression. Furthermore, the inhibition of miR-497 antagonized the suppressive
effect of SNHG16-depleted cells on cell proliferation, migration, and invasion.
Conclusion: These
findings revealed that SNHG16 drived the PTC progression possibly via
regulating miR-497, suggesting that SNHG16 might be a novel therapeutic agent
for PTC.
Keywords: papillary
thyroid cancer, long noncoding RNAs, SNHG16, miR-497