110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

环状 RNA hsa_circ_0072309 通过靶向 miR-492 抑制乳腺癌细胞的增殖和侵袭
Authors Yan L, Zheng M, Wang H
Received 8 September 2018
Accepted for publication 19 November 2018
Published 22 January 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 1033—1041
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S186857
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonella D'Anneo
Background: Although
the number of circular RNAs (circRNAs) that has been identified in multiple
cancer tissues continues to increase, the relationship between circRNA
expression and carcinogenesis remains unknown. The role of hsa_circ_0072309 in
breast cancer has remained undefined until now. In this study, we aimed to
investigate the role of hsa_circ_0072309 in breast cancer progression.
Methods: hsa_circ_0072309
expression in breast cancer tissues was analyzed using qRT-PCR. A series of
functional experiments were carried out to investigate hsa_circ_0072309
function in breast cancer development and its underlying molecular mechanisms.
Results: hsa_circ_0072309
expression in breast cancer tissues was upregulated relative to that in
adjacent normal tissues. hsa_circ_0072309 could serve as a prognostic biomarker
of breast cancer. hsa_circ_0072309 overexpression dramatically inhibited the
proliferation, migration, and invasion of breast cancer cells in vitro. In vivo
assays revealed that the ectopic expression of hsa_circ_0072309 repressed
breast cancer growth. The results of our mechanistic studies indicated that
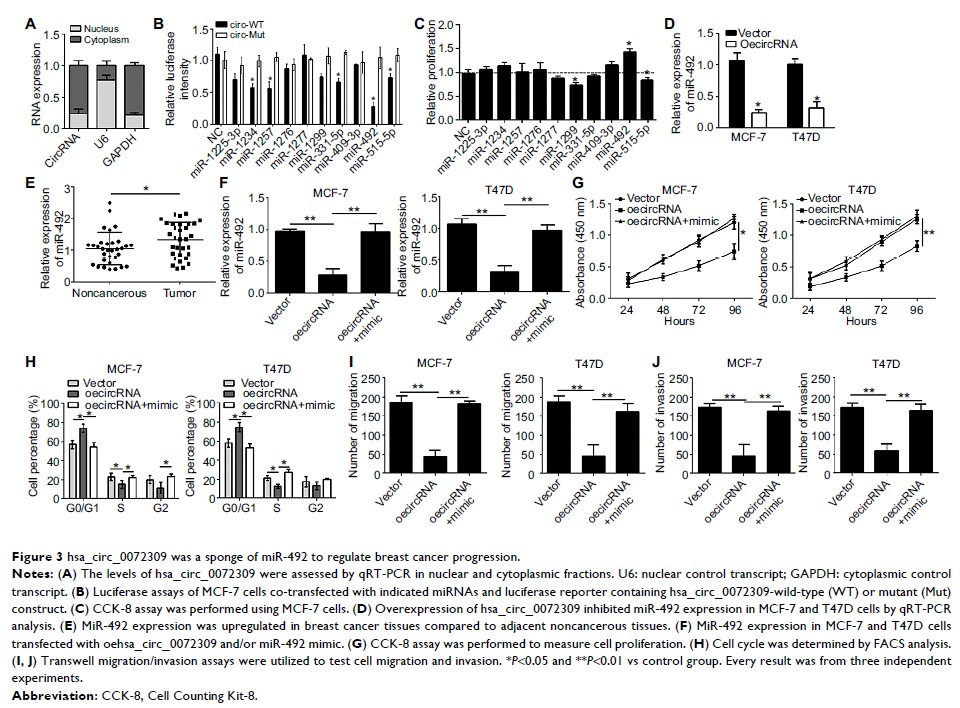
hsa_circ_0072309 could act as the sponge of miR-492, which exhibited increased
expression in breast cancer tissues. Hsa_circ_0072309 suppressed breast cancer cell
proliferation, migration, and invasion by inhibiting miR-492.
Conclusion: Our
findings revealed for the first time that the hsa_circ_0072309-miR-492 axis
plays an essential role in breast cancer progression.
Keywords: circular
RNA, hsa_circ_0072309, miR-492, breast cancer, progression