110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

急性髓细胞白血病细胞中高三尖杉酯碱和依托泊苷的协同性细胞毒性与抗氧化防御的破坏有关
Authors Zhang J, Geng H, Liu L, Zhang H
Received 14 September 2018
Accepted for publication 14 November 2018
Published 22 January 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 1023—1032
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S187597
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Ahmet Emre Eskazan
Background/Aims: Cytotoxicity
induced by reactive oxygen species (ROS) is critical for the effectiveness of
chemotherapeutic drugs used in the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia (AML).
This study aimed to investigate whether ROS contributes to cytotoxicity in AML
cells when treated with homoharringtonine (HHT) and etoposide (ETP) in
combination.
Methods: AML cell
lines THP1 and HL60 and primary AML cells from patients were treated with HHT
and ETP alone or in combination, and cell viability was determined by trypan
blue exclusion test, and apoptosis was analyzed by annexin-V/propidium iodide
double staining as well as Western blot for measuring expression of cleaved
caspase-9 and cleaved caspase-3. Intracellular ROS level was detected by
DCFH-DA fluorescence assay, and N-Acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC) was used to scavenge
intracellular ROS. Retroviral infection was applied to mediate stable
overexpression in AML cells.
Results: We show
that HHT and ETP exhibit synergistic cytotoxicity in AML cell lines and primary
AML cells in vitro, and meanwhile, HHT causes elevated ROS generation in
ETP-treated AML cells. We next reveal that the elevated ROS is a critical
factor for the synergistic cytotoxicity, since ROS scavenge by NAC remarkably
diminishes this effect. Mechanistically, we demonstrate that HHT causes
elevated ROS generation by disabling thioredoxin-mediated antioxidant defense.
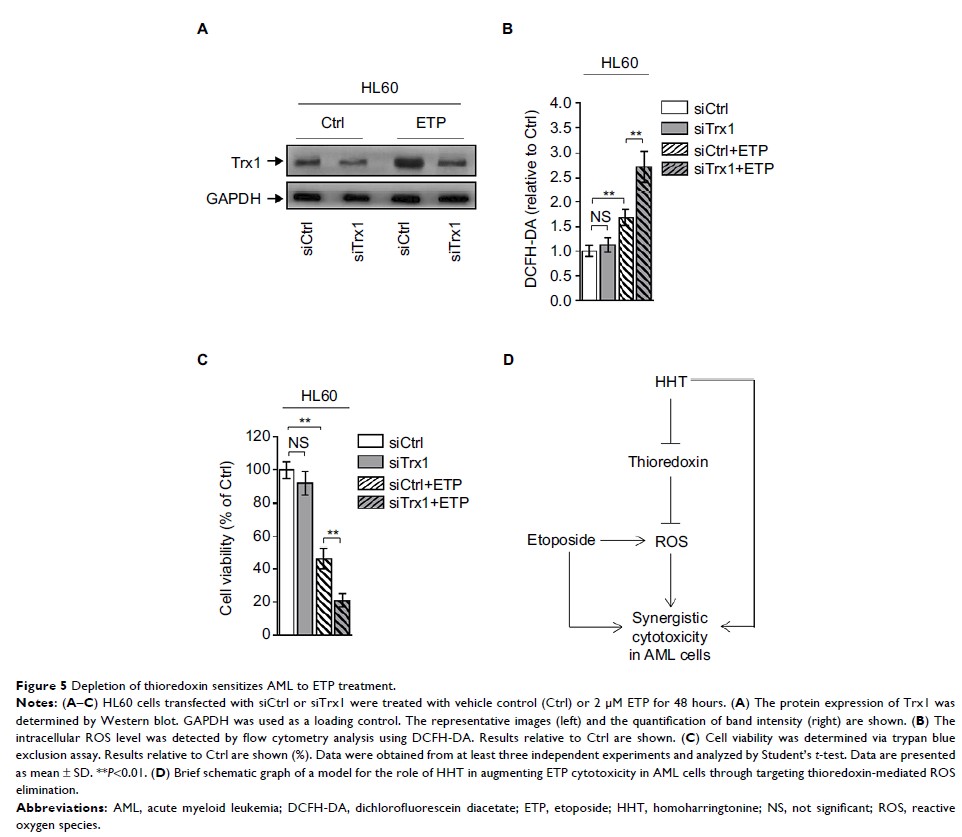
Finally, similar to HHT treatment, depletion of thioredoxin sensitizes AML to
ETP treatment.
Conclusion: These
results provide the foundation for augmenting the efficacy of ETP in treating
AML with HHT, and also highlight the importance of targeting ROS in improving
treatment outcome in AML.
Keywords: homoharringtonine,
etoposide, synergistic cytotoxicity, acute myeloid leukemia, antioxidant
defense, reactive oxygen species, thioredoxin