110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

MicroRNA-339 通过靶向 ZNF689 抑制人肝细胞癌的增殖和侵袭
Authors Zeng H, Zheng J, Wen S, Luo J, Shao G, Zhang Y
Received 4 September 2018
Accepted for publication 28 December 2018
Published 22 January 2019 Volume 2019:13 Pages 435—445
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S186352
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sukesh Voruganti
Background: Hepatocellular
carcinoma (HCC) is the second leading cause of cancer mortality worldwide,
however, the prognosis for HCC remains unsatisfactory. This study aimed to
explore the role of miR-339-5p in HCC.
Methods: We first
used quantitative real-time PCR to examine the level of miR-339-5p in HCC
tissues. Then we further adopted Western blotting assay, CCK8, cell invasion
assays, apoptosis detection assay, and luciferase assay to analyze how it
mediate the development of HCC.
Results: We found
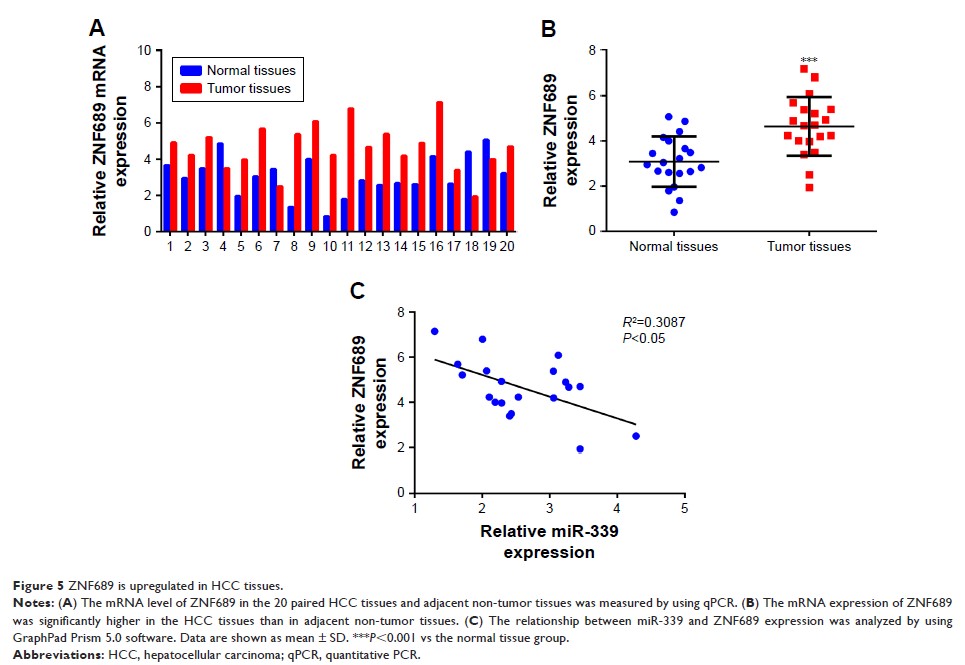
that miR-339 is significantly decreased in primary HCC tissues. Overexpression
of miR-339 in HCC cells remarkably suppressed proliferation and invasion and
induced apoptosis. However, silencing miR-339 in HCC cells promoted proliferation
and invasion, and reduced apoptosis. Moreover, we demonstrated that ZNF689 is a
target of miR-339 and there is a negative correlation between miR-339 and
ZNF689 expression in the HCC tissues. Overexpression of ZNF689 in
miR-339-overexpressing HCC cells partially antagonized the inhibitory effects
of miR-339.
Conclusion: Our study
revealed that miR-339 inhibits HCC growth through targeting oncoprotein ZNF689
and restoration of miR-339 might be feasible therapeutic strategy for HCC
treatment.
Keywords: miR-339-5p,
HCC, ZNF689, treatment, proliferation