110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

通过靶向 Ras/MEK/ERK 通路激活 1, 25-(OH)2D3 对人乳腺癌细胞株的抗癌活性
Authors Zheng W, Cao L, Ouyang L, Zhang Q, Duan B, Zhou W, Chen S, Peng W, Xie Y, Fan Q, Gong D
Received 10 October 2018
Accepted for publication 4 December 2018
Published 22 January 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 721—732
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S190432
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjeev Srivastava
Purpose: Breast cancer
is the most common cancer among women with ~1.67 million cases diagnosed
annually worldwide, and ~1 in 37 women succumbed to breast cancer. Over the
past decades, new therapeutic strategy has substantially improved the curative
effect for women with breast cancer. However, the currently available
ER-targeted and HER-2-based therapies are not effective for triple-negative
breast cancer patients, which account for ~15% of total breast cancer cases.
Materials and methods: We
reported that 1,25-(OH)2D3, a biologically active form of vitamin D3, exhibited a
strong anticancer effects on the proliferation, migration, invasion, cell cycle
arrest, and apoptosis of both ER-positive (MCF-7) and ER-negative breast cancer
cells (MDA-MB-453).
Results: The
anticancer effect of 1,25-(OH)2D3 was more potent compared to the classical
chemotherapeutics tamoxifen in MDA-MB-453 cells. Furthermore, we also found
that 1,25-(OH)2D3 decreased the expression of Ras and resulted in
decrease of the phosphorylation of downstream proteins MEK and ERK1/2,
indicating that 1,25-(OH)2D3 plays its anticancer roles through
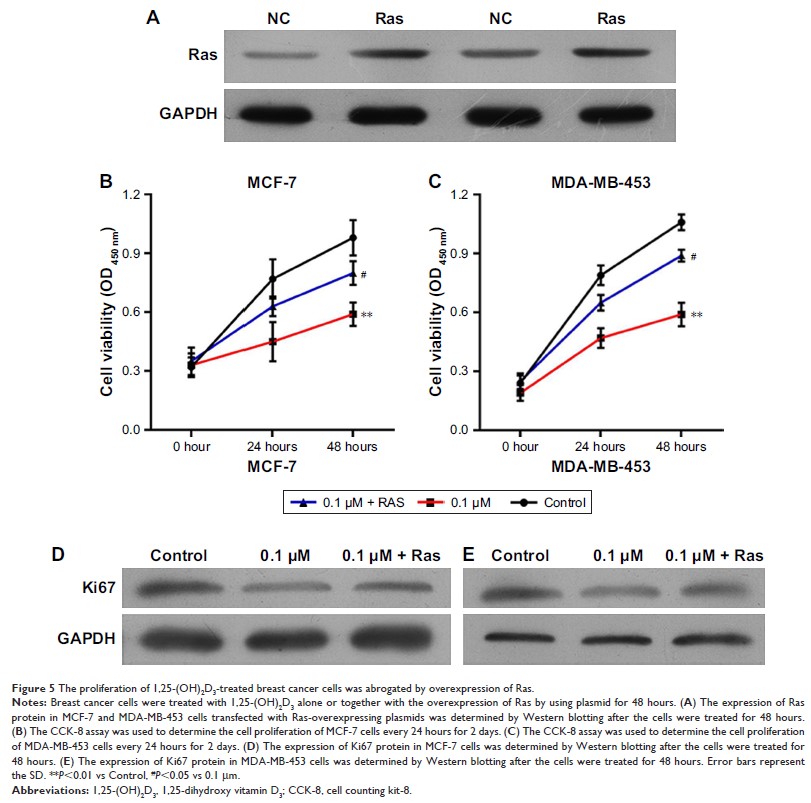
targeting the Ras/MEK/ERK signaling pathway. In addition, Ras overexpression abrogated
1,25-(OH)2D3-induced G0/G1 cell cycle arrest and apoptosis
of breast cancer cells, as well as the suppression of proliferation, migration,
and invasion. Our study suggested that 1,25-(OH)2D3 suppressed
breast cancer tumorigenesis by targeting the Ras/MEK/ERK signaling pathway.
Conclusion: 1,25-(OH)2D3 might
serve as a promising supplement for breast cancer drug therapy, especially for
the ER-negative breast cancer and drug-resistant breast cancer.
Keywords: breast
cancer, 1,25-(OH)2D3, ER-negative, cell apoptosis, cell
proliferation