110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

可切除性胰腺癌的新辅助治疗与前期手术的比较:汇总分析和系统回顾
Authors Ren X, Wei X, Ding Y, Qi F, Zhang Y, Hu X, Qin C, Li X
Received 13 October 2018
Accepted for publication 21 December 2018
Published 22 January 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 733—744
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S190810
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Takuya Aoki
Objective: The role
of neoadjuvant therapy (NAT) in resectable pancreatic cancer (RPC) remains
controversial. Therefore, this meta-analysis was performed to compare the
clinical differences between NAT and upfront surgery in RPC.
Materials and methods: A
systematic literature search was performed in PubMed, Embase, Web of Science,
and the Cochrane Register of Controlled Trials databases. Only patients with
RPC who underwent tumor resection and received adjuvant or neoadjuvant treatment
were enrolled. The OR or HR and 95% CIs were calculated employing fixed-effects
or random-effects models. The HR and its 95% CI were extracted from each
article that provided survival curve. Publication bias was estimated using
funnel plots and Egger’s regression test.
Results: In total,
eleven studies were included with 9,386 patients. Of these patients, 2,508
(26.7%) received NAT. For patients with RPC, NAT resulted in an increased R0
resection rate (OR=1.89; 95% CI=1.26–2.83) and a reduced positive lymph node
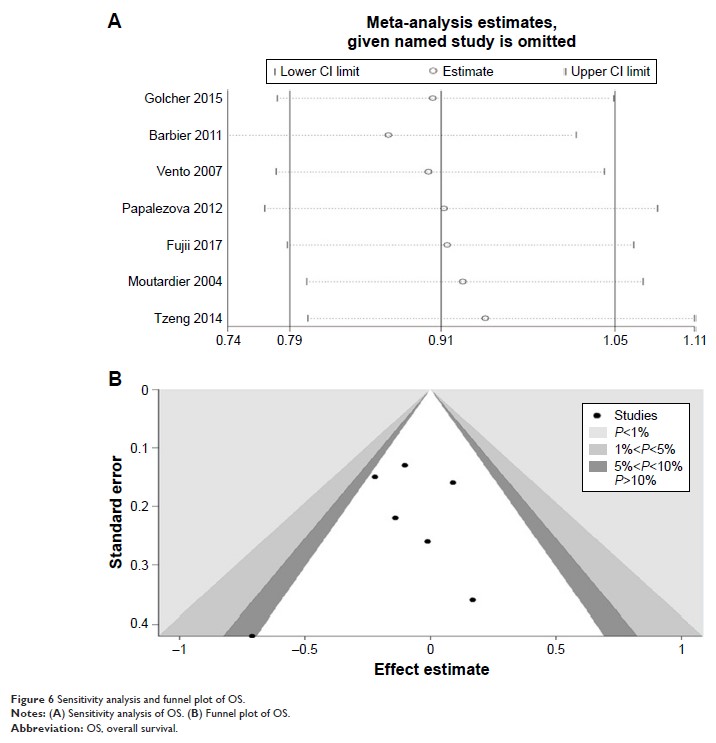
rate (OR=0.34; 95% CI=0.31–0.37) compared with upfront surgery. Nevertheless,
patients receiving NAT did not exhibit a significantly increased overall
survival (OS) time (HR=0.91; 95% CI=0.79–1.05).
Conclusion: In
patients with RPC, R0 resection rate and positive lymph node rate after NAT
were superior to those of patients with upfront surgery. The NAT group
exhibited no significant effect on OS time when compared with the upfront
surgery group. However, this conclusion requires more clinical evidence to
improve its credibility.
Keywords: neoadjuvant
therapy, resectable, pancreatic, neoplasm, prognosis, meta-analysis