110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

非诺贝特通过 AKT/NF-κB 通路调节细胞凋亡,增强对人乳腺癌细胞的化学敏感性
Authors Sun J, Zheng Z, Chen Q, Pan Y, Quan M, Dai Y
Received 17 October 2018
Accepted for publication 21 December 2018
Published 23 January 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 773—783
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S191239
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjeev Srivastava
Background: Cumulatively,
evidences revealed that fenofibrate used in the therapy of hyperlipidemia and
hypercholesterolemia has anti-cancer effect in multiple cancer types. However,
its function and underlying mechanism of chemosensitization in breast cancer
remain poorly understood.
Materials and methods: The
cytotoxicity of fenofibrate and anti-cancer drugs in breast cancer cells was
determined by MTT. Apoptosis and mitochondrial membrane potential were measured
using flow cytometry. Caspases and PARP cleavage, the Bcl-2 family members’
protein expression, as well as the activation of AKT and NF-κB signaling
pathways were evaluated using Western blot assay. Real-time PCR was used to
determine the mRNA expression of Bcl-2 family members.
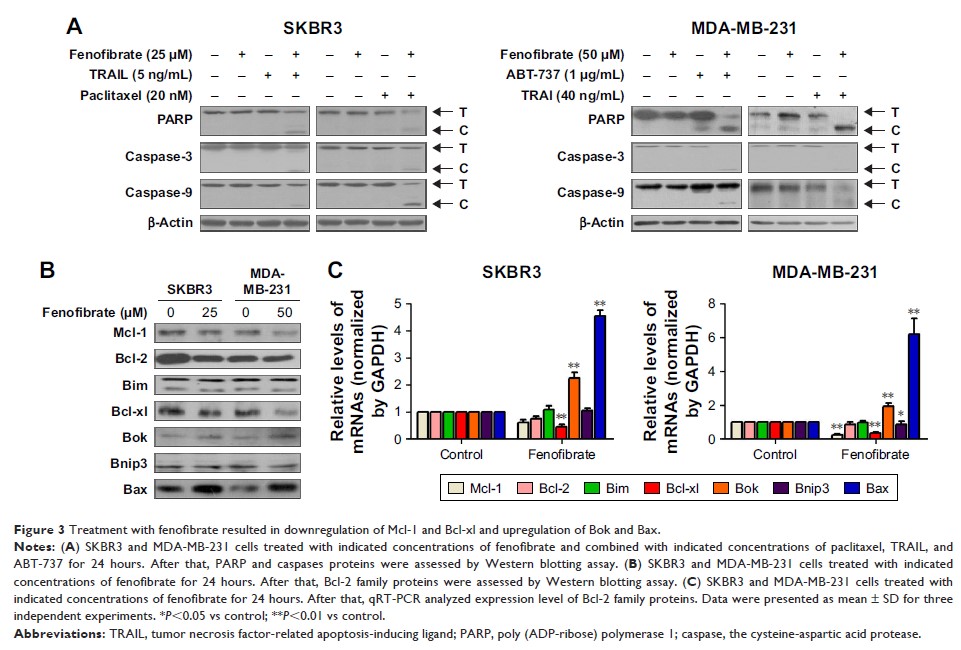
Results: Our data
indicated that fenofibrate suppressed SKBR3 and MDA-MB-231 cell growth in a
dose-dependent manner, in the same way as paclitaxel, tumor necrosis
factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL), ABT-737, and doxorubicin.
Subtoxic levels of fenofibrate significantly augmented paclitaxel, TRAIL,
ABT-737, and doxorubicin-induced apoptosis in both these two cell lines.
Fenofibrate-promoted chemosensitivity is predominantly mediated by caspase-9
and caspase-3 activation and mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization.
Meanwhile, chemosensitivity promoted by fenofibrate also increased the
expression of Bax and Bok and decreased the expression of Mcl-1 and Bcl-xl.
Mechanistically, fenofibrate effectively reduced the phosphorylation levels of AKT
and NF-κB. In addition, imiquimod, an NF-κB activator, could reverse
fenofibrate-induced susceptibility to ABT-737-triggered apoptosis.
Conclusion: The
present study provided the evidence of the underlying mechanisms on
chemosensitization of fenofibrate by inducing the apoptosis of breast cancer in
an AKT/NF-κB-dependent manner and implicated the potential application of
fenofibrate in potentiating chemosensitivity in breast cancer therapy.
Keywords: human
breast cancer, fenofibrate, chemosensitization, AKT, NF-κB