110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

环境空气污染对中国北京慢性阻塞性肺疾病入院的短期影响(2013–2017)
Authors Gao N, Li C, Ji J, Yang Y, Wang S, Tian X, Xu KF
Received 27 September 2018
Accepted for publication 13 December 2018
Published 23 January 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 297—309
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/COPD.S188900
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Chunxue Bai
Purpose: Evidence
between air pollution and COPD admissions is inconsistent and limited in China.
In this study, we aimed to explore the effects of air pollutants on COPD
admissions in Beijing, China.
Patients and methods: Daily
COPD hospital admission visits derived from tertiary and secondary hospitals in
Beijing were retrieved from January 2013 to February 2017. Air pollutant levels
and meteorological data over the same periods were also achieved. Generalized
additive model was applied to estimate the percentage changes with 95% CIs in
daily admissions corresponding to 10 µg/m3 increases
in pollutants levels [1 mg/m3 in carbon monoxide (CO)], stratified by
age, gender, and season.
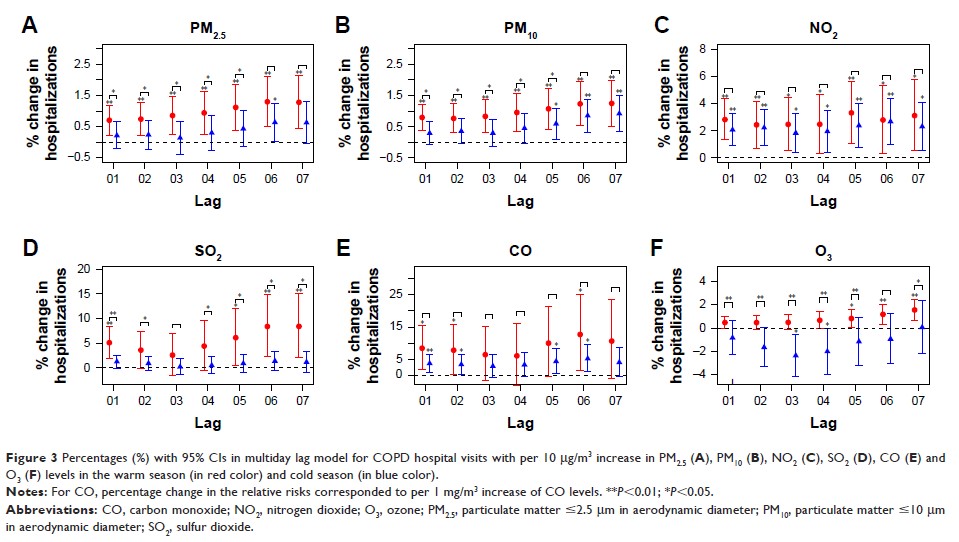
Results: Seventy-three
thousand seventy-six COPD hospital admission visits were included with mean
daily visits of 48 (21). Cumulative lag effect with per 10 µg/m3 increase
in air pollutant levels was largest for nitrogen dioxide (NO2) with 3.03%
(95% CI: 1.82%–4.26%) at lag 06, for sulfur dioxide (SO2) with 2.07%
(95% CI: 1.00%–3.15%) at lag 01, for particulate matter ≤10 µm in aerodynamic
diameter (PM10) with 0.92% (95% CI: 0.55%–1.30%) at lag 07,
and for particulate matter ≤2.5 µm in aerodynamic diameter (PM2.5) with 0.82%
(95% CI: 0.38%–1.26%) at lag 06, respectively. Percentage increase for each 1
mg/m3 increase in CO was 5.99% (95% CI:
2.74%–9.34%) at lag 06. Further, stronger effects on COPD admissions were found
in warm seasons than in cold seasons.
Conclusion: Short-term
exposures to PM2.5, PM10, NO2, SO2, and CO had
adverse effects on COPD hospitalizations in Beijing with different magnitudes
and lag days.
Keywords: adverse
effects, air pollution, COPD, time series analysis, hospital visits