110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

通过卵磷脂 - 壳聚糖纳米粒负载紫杉醇胆固醇复合物改善姑息性肿瘤内注射治疗的抗肿瘤效果
Authors Chu XY, Huang W, Wang YL, Meng LW, Chen LQ, Jin MJ, Chen L, Gao CH, Ge C, Gao ZG, Gao CS
Received 25 September 2018
Accepted for publication 1 December 2018
Published 23 January 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 689—705
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S188667
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Govarthanan Muthusamy
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Mian Wang
Background: Intratumoral
injection is a palliative treatment that aims at further improvement in the
survival and quality of life of patients with advanced or recurrent carcinomas,
or cancer patients with severe comorbidities or those with a poor performance
status.
Methods: In this
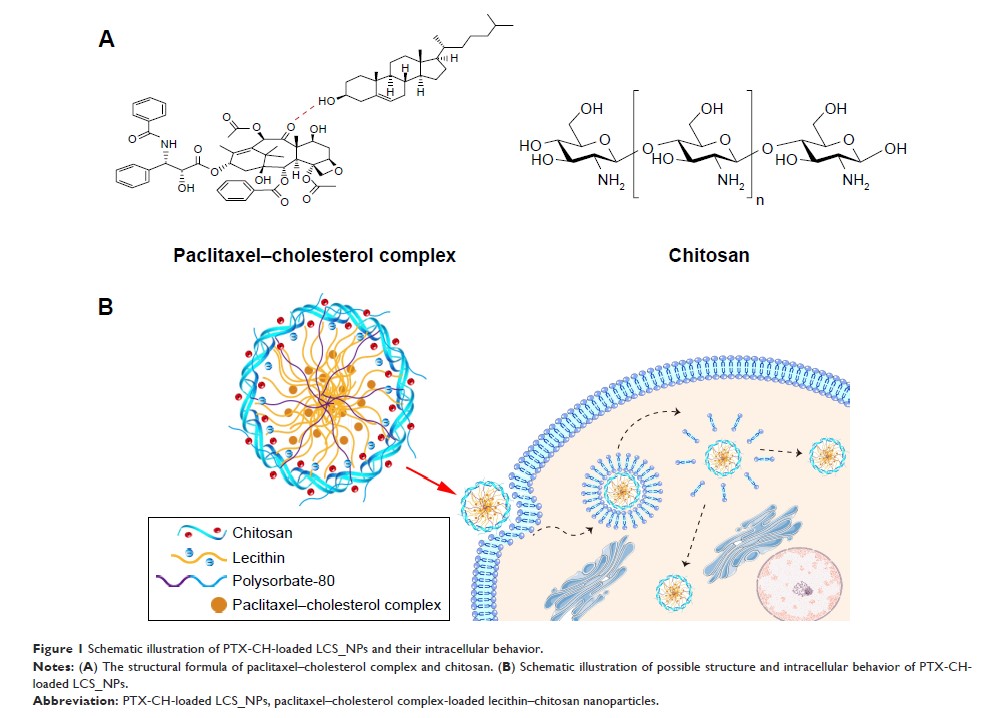
study, a solvent-injection method was used to prepare paclitaxel–cholesterol complex-loaded
lecithin–chitosan nanoparticles (PTX-CH-loaded LCS_NPs) for intratumoral
injection therapy, and the physicochemical properties of NPs were well
characterized.
Results: The
particle size and zeta potential of PTX-CH-loaded LCS_NPs were 142.83±0.25 nm
and 13.50±0.20 mV, respectively. Release behavior of PTX from PTX-CH-loaded
LCS_NPs showed a pH-sensitive pattern. The result of cell uptake assay showed
that PTX-CH-loaded LCS_NPs could effectively enter cells via the
energy-dependent caveolae-mediated endocytosis and macropinocytosis in company
with the Golgi apparatus. Meanwhile, PTX-CH-loaded LCS_NPs had a better ability
to induce cell apoptosis than PTX solution. The in vivo antitumor results
suggested that PTX-CH-loaded LCS_NPs effectively inhibited mouse mammary cancer
growth and metastasis to distant organs and significantly improved the survival
rate of tumor-bearing mice by intratumoral administration.
Conclusion: In
general, our study demonstrated that PTX-CH-loaded LCS_NPs used for palliative
treatment by intratumoral injection showed improved safety and antitumor
efficacy, which provided an alternative approach in the field of palliative
chemotherapy.
Keywords: lecithin,
chitosan, paclitaxel, nanoparticles, pH responsive, palliative chemotherapy,
intratumoral injection