110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

早期应用胰岛素样生长因子-1 对脓毒性脑病认知功能的影响
Authors Yang Y, Liang S, Li Y, Gao F, Cao Y, Zhao X, Gao G, Li L
Received 14 October 2018
Accepted for publication 17 December 2018
Published 23 January 2019 Volume 2019:15 Pages 323—337
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S190845
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Jun Chen
Background: Both
protective and therapeutic functions of insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) in
brain injury have been reported, but its effects on cognitive sequelae after
septic encephalopathy (SE) remain unclear.
Materials and methods: This
study was divided into three parts, and a septic model was built by cecal
ligation and puncture (CLP). First, survival analysis was performed, and
IGF-1’s effects on long-term cognition and depressive emotion were assessed.
Second, the characteristics of IGF-1 function in cognition were evaluated.
Finally, cytochrome C, caspase-9, tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNFR), and
caspase-8 levels as well as cell apoptosis in the hippocampus were evaluated.
Results: IGF-1 did
not reduce mortality or alleviate depressive symptoms in septic rats, but
improved the memory of noxious stimulation and spatial learning and memory.
These effects were observed only when IGF-1 was administered within 0–6 hours
after CLP. Moreover, cytochrome C and caspase-9 expression levels were increased
at 6 hours after CLP in the hippocampus, while TNFR and caspase-8 amounts were
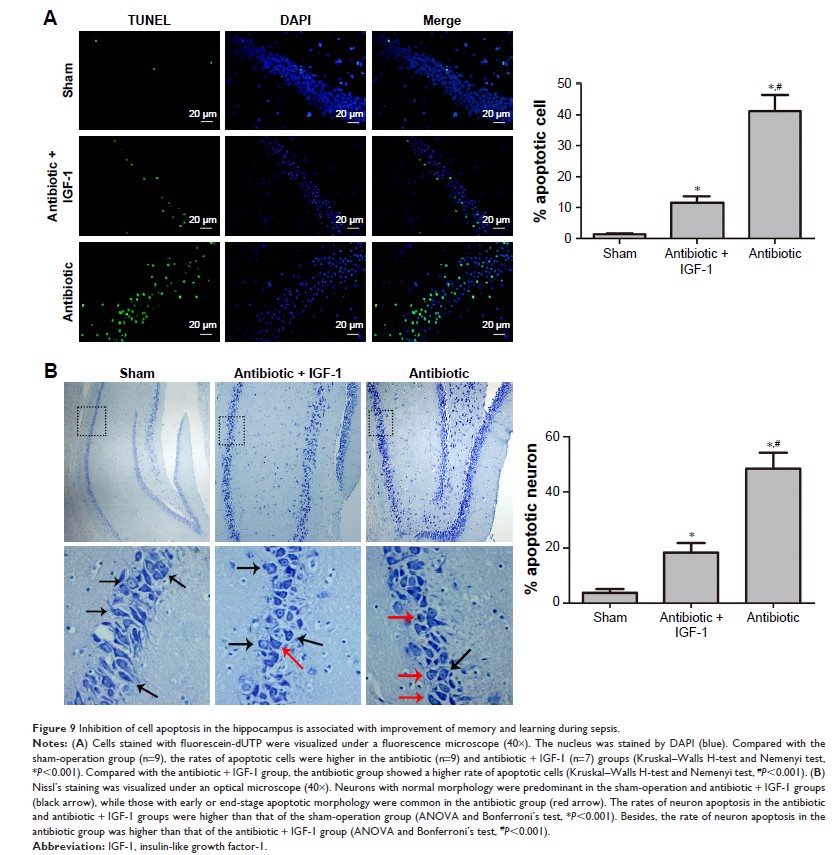
not increased until 12 hours after CLP. Cell apoptosis increased at 12 hours
after CLP, but was inhibited by IGF-1.
Conclusion: Cognitive
impairment in rats recovering from SE is associated with cell apoptosis in the
hippocampus. Supplementation of IGF-1 reduces cell apoptosis by preventing the
over-expression of cytochrome C and TNFR, and results in improved cognitive
function. However, improvement only occurs when IGF-1 is administered at the
early stage (within 6 hours) of sepsis. As cytochrome C activation occurs
earlier than that of TNFR in this study, cytochrome C may be the main factor
inducing apoptosis in early SE.
Keywords: septic
encephalopy, memory, learning, IGF-1, cytochrome C, TNFR, apoptosis