110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

MicroRNA-505 通过直接靶向 Polo 样激酶 1 来遏制胃癌细胞的增殖和侵袭
Authors Dang SC, Wang F, Qian XB, Abdul M, Naseer QA, Jin W, Hu R, Gu Q, Gu M
Received 2 October 2018
Accepted for publication 19 December 2018
Published 24 January 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 795—803
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S189521
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr William Cho
Purpose: The
expression of microRNA-505 (miR-505) has been investigated in various cancers;
however, its effect and mechanism in relation to gastric cancer (GC) are yet to
be determined. Thus, the current evaluation aimed to examine the expression and
potential role of miR-505 in GC.
Materials and methods: Quantitative
real-time PCR was carried out to analyze miR-505 expression in GC cells and
tissues. We observed that miR-505 is differentially expressed in GC cells
following transfection of its mimics or inhibitors. Changes in cell invasion,
cell proliferation, and epithelial–mesenchymal transition markers were
measured.
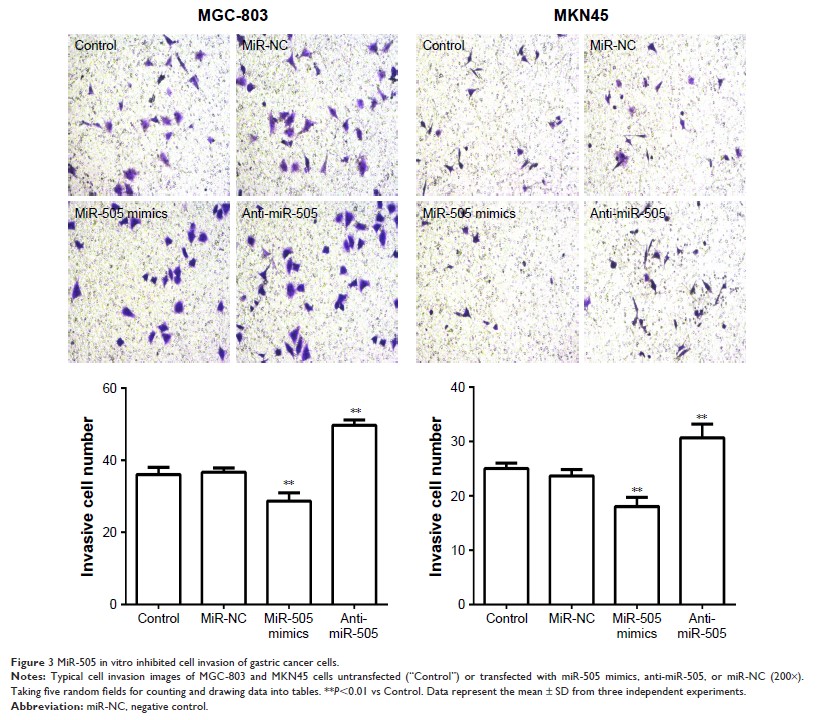
Results: These
findings indicated that miR-505 expression is downregulated in both GC cell
lines and GC tissues. In addition, knockdown miR-505 induced the invasion and
proliferation of GC cells. Transfection of miR-505 mimics led to an elevation
in N-cadherin expression but a decrease in E-cadherin expression. Furthermore,
we have shown that miR-505 binds to the 3'-UTR region of Polo-like kinase-1.
Conclusion: Our
results indicated that miR-505 suppresses GC cell proliferation and invasion;
it may be a valuable candidate gene for seeking therapy strategy for GC.
Keywords: MicroRNA-505,
EMT, polo-like kinase-1, gastric cancer