110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

lncRNA 小核仁 RNA 宿主基因 20 预测胶质瘤预后不良,并通过沉默 P21 促进细胞增殖
Authors Li XS, Shen FZ, Huang LY, Hui L, Liu RH, Ma YJ, Jin BZ
Received 29 October 2018
Accepted for publication 3 January 2019
Published 24 January 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 805—814
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S192641
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Leo Jen-Liang Su
Background: In
multiple cancers, long non-coding RNA small nucleolar RNA host gene 20 (lncRNA SNHG20 ) is
generally dysregulated. In the present study, both the biological role and
clinicopathological value of lncRNA SNHG20 in glioma are explored.
Methods: Real-time
PCR was employed to determine lncRNA SNHG20 expression in glioma patients. The
prognostic role of expression of lncRNA SNHG20 was evaluated in a retrospective
cohort study. In addition, the association between lncRNA SNHG20 expression
and the clinicopathological features of glioma patients, such as tumor
recurrence, survival status, follow-up time, WHO grade, resection extent, tumor
location, Karnofsky performance scale score, cystic change, tumor size, gender
and age, was discussed. By constructing and transfecting siRNAs that
targeted lncRNA
SNHG20 into the glioma U87 cells, the effects of lncRNA SNHG20 on
the proliferation and cell cycle of U87 cells were assessed through cell
counting kit-8, colony formation and cell cycle assays, respectively. In
addition, Western blot and real-time PCR measured the expression levels of P21
and CCNA1 in U87 cells after being transfected with SNHG20 siRNA.
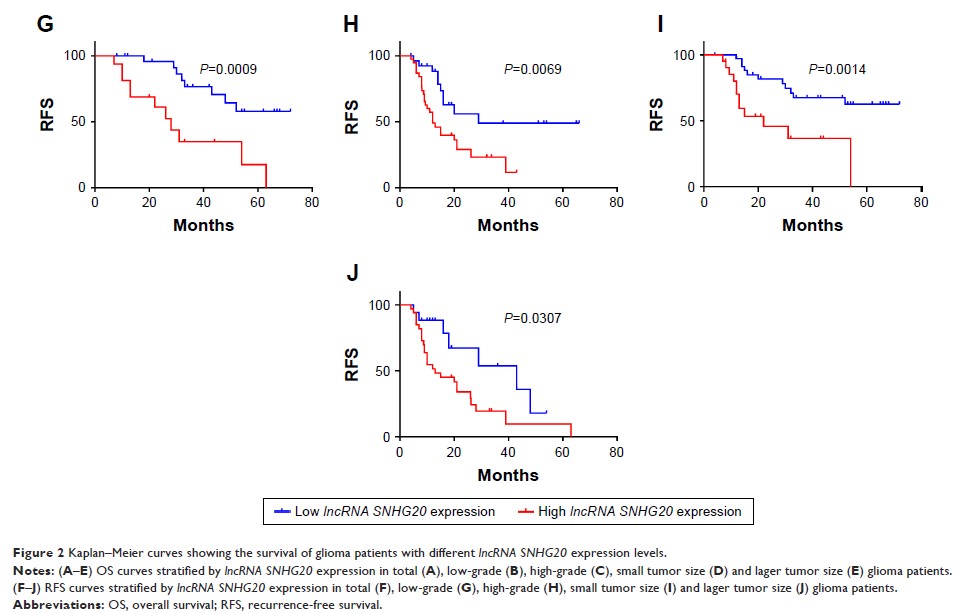
Results: Our
results suggested the high expression of lncRNA SNHG20 in
human glioma tissues compared with normal brain tissues, which was related to
recurrence-free survival and poor overall survival in glioma patients.
According to the existing retrospective cohort study, high lncRNA SNHG20 expression
was associated with tumor size, extent of resection, WHO grade, follow-up time,
survival status and recurrence. Besides, knocking down the expression of lncRNA SNHG20 could
inhibit the proliferation and colony formation abilities of glioma U87 cells
through cell cycle arrest. Consequently, the expression of CCNA1 was inhibited,
and the expression of P21 was up-regulated in U87 cells.
Conclusion: A
high lncRNA
SNHG20 expression level predicts the poor prognosis for glioma
patients. Moreover, lncRNA SNHG20 can promote glioma
proliferation through silencing P21 and thus lncRNA SNHG20 is
an independent potential prognostic biomarker for glioma patients.
Keywords: lncRNA SNHG20 ,
glioma, clinicopathological, prognosis, proliferation