110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

miRNA-101-5p 通过靶向 CXCL6 抑制 NSCLC 细胞的生长和侵袭性
Authors Chen Q, Liu D, Hu Z, Luo C, Zheng SL
Received 16 August 2018
Accepted for publication 26 October 2018
Published 25 January 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 835—848
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S184235
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Leo Jen-Liang Su
Background: The
purpose of this study is to explore the potential biological roles of
miR-101-5p in the progression of non-small-cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC).
Methods: The
levels of miR-101-5p and chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 6 (CXCL6) in NSCLC
tissues and cells were detected using the quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR)
assay. Proliferation, colony formation, migration and invasion assays were
conducted using miR-101-5p-transfected NSCLC cells in vitro. The
expression of CXCL6 was measured using immunofluorescence assay. Xenograft
model and lung metastasis model were constructed to further reveal the precise
roles of miR-101-5p in the lung metastasis and growth of NSCLC cells
in vivo.
Results: miR-101-5p
was underregulated in NSCLC tissues when compared with that in the normal
controls. The levels of miR-101-5p were lower in NSCLC cells (H1975, A549,
HCC827 and H1650) than in non-tumorigenic human bronchial epithelial cells
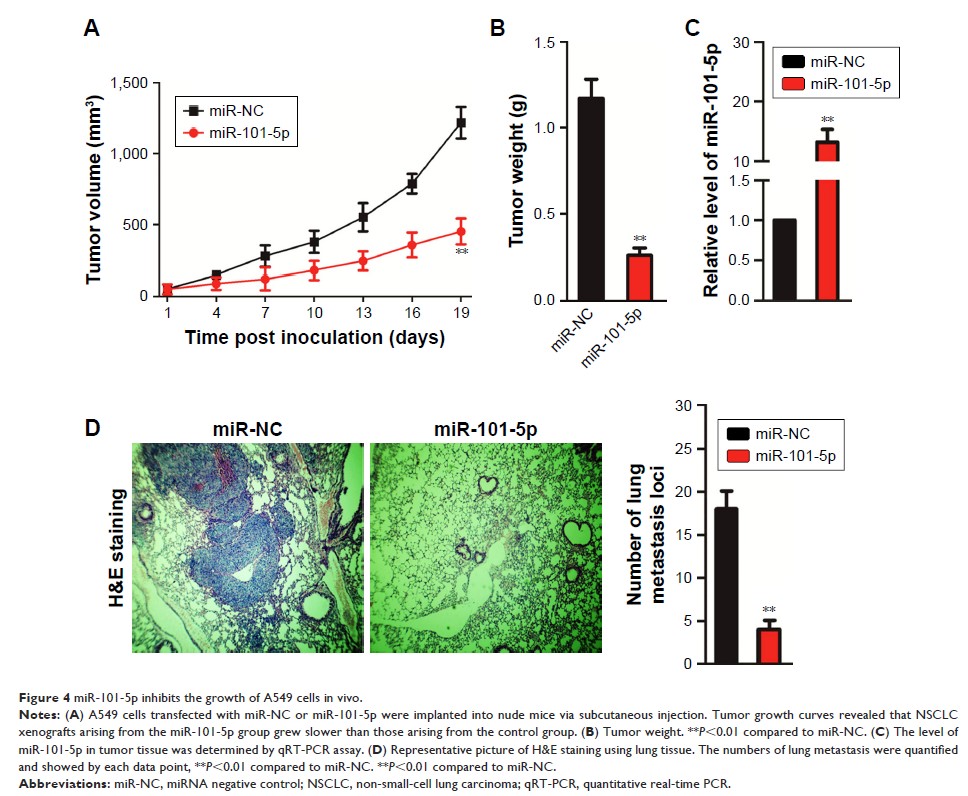
(BEAS-2B). Overregulation of miR-101-5p restrained the aggressiveness
phenotypes of NSCLC cells in vitro. Furthermore, overregulation of
miR-101-5p reduced the tumor growth and pulmonary metastasis of NSCLC cells
in vivo. CXCL6 was the target gene of miR-101-5p in NSCLC. The mRNA levels
of CXCL6 were negatively associated with the levels of miR-101-5p in NSCLC
tissues. Finally, the rescue experiments suggested that the inhibitory role of
miR-101-5p was mediated by regulating the expression of CXCL6 in NSCLC.
Conclusion: These
findings indicated that overregulation of miR-101-5p restrained the progression
of NSCLC cells by targeting CXCL6 and might function as a potential therapeutic
target for NSCLC.
Keywords: lung
cancer, miR-101-5p, CXCL6, metastasis