110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

MiR-206 通过靶向 MUC1 基因抑制胃癌细胞的增殖、迁移和侵袭
Authors Deng M, Qin Y, Chen X, Wang Q, Wang J
Received 12 July 2018
Accepted for publication 12 October 2018
Published 25 January 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 849—859
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S180021
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Federico Perche
Background: MicroRNAs
(miRNAs) can regulate the post-transcriptional level of gene expression. It has
been documented that downregulation of miR-206 is significant in human gastric
cancer (GC), whereas its role in GC cell biological behaviors, including
proliferation, migration, and invasion, has not been thoroughly investigated.
MiR-206 levels have a negative association with lymph node metastasis and tumor
invasion, and patients with higher miR-206 expression have better prognoses.
Functional studies demonstrated that miR-206 overexpression significantly
suppresses GC cell proliferation, migration, and invasion, and induces
apoptosis in vitro.
Materials and methods: MiR-206
and MUC1 were determined by RNA extraction, quantitative real-time polymerase
chain reaction, and luciferase reporter gene assays. The viability of GC cells
was tested using the Cell Counting Kit 8 assay. Transwell invasion and
migration assays detected GC cancer cell proliferation, invasion, and
migration. Flow cytometry was applied to analyze apoptotic cells. FACS analysis
was applied to detect the mitochondrial membrane potential of cells. Western
blotting assay determined protein levels.
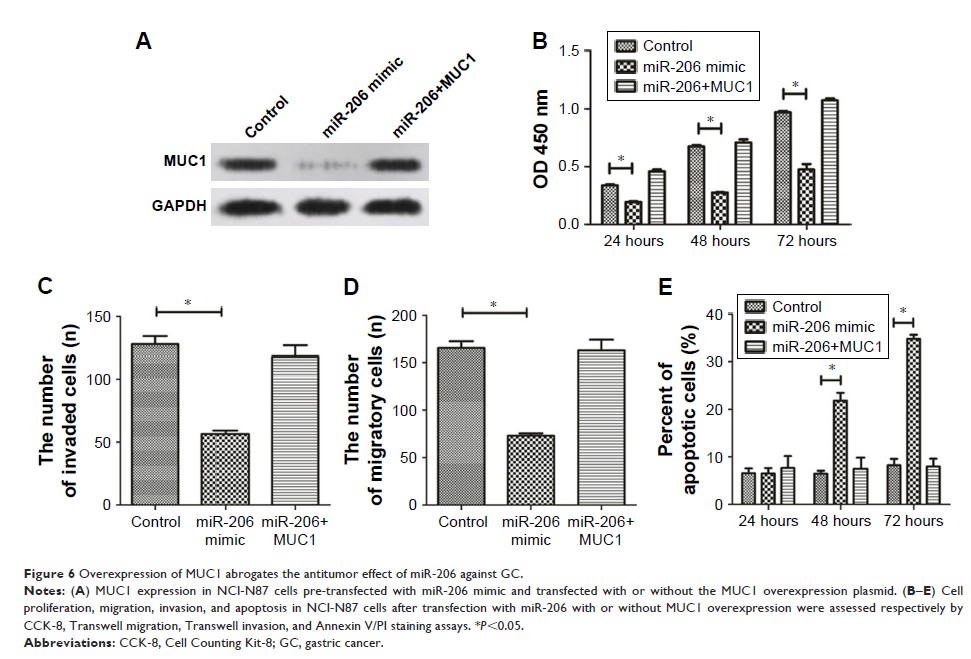
Results: The
luciferase reporter gene assay demonstrated that miR-206 might directly bind to
the 3'UTR of the MUC1 gene and suppress MUC1 expression.
Furthermore, MUCI expression was upregulated and inversely associated with
miR-206 levels in GC tissues. More importantly, the miR-206-mediated
suppression of proliferation, migration, and invasion, and the induction of
apoptosis, were abrogated by MUC1 overexpression.
Conclusion: Our data
demonstrated that miR-206 may exert antitumor activities through inhibiting the
expression of MUC1, which may serve as an effective and potential target for GC
treatment.
Keywords: miR-206,
MUC1, gastric cancer, metastasis