110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

高压氧疗法通过 Akt/GSK3β/β-catenin 通路减轻创伤性脑损伤诱导的神经细胞凋亡
Authors He H, Li X, He Y
Received 12 August 2018
Accepted for publication 27 October 2018
Published 25 January 2019 Volume 2019:15 Pages 369—374
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S183632
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yu-Ping Ning
Background: Given
that the therapeutic effect of hyperbaric oxygen (HBO) therapy on traumatic
brain injury (TBI) has been debated for a long time, it is necessary to clarify
the mechanism underlying the effect of HBO on acute TBI.
Methods: This
study investigated the effect of HBO therapy on neuronal apoptosis induced by
acute TBI using the mouse model of TBI. The number of apoptotic cells and
expression of apoptosis-associated factors (including caspase 3, pAkt/Akt,
pGSK3β/GSK3β, and β-catenin) in pericontusional cortices of mice exposed to
sham, TBI, and TBI + HBO treatment were measured and analyzed using TUNEL
assay, quantitative reverse-transcription PCR, and Western blot.
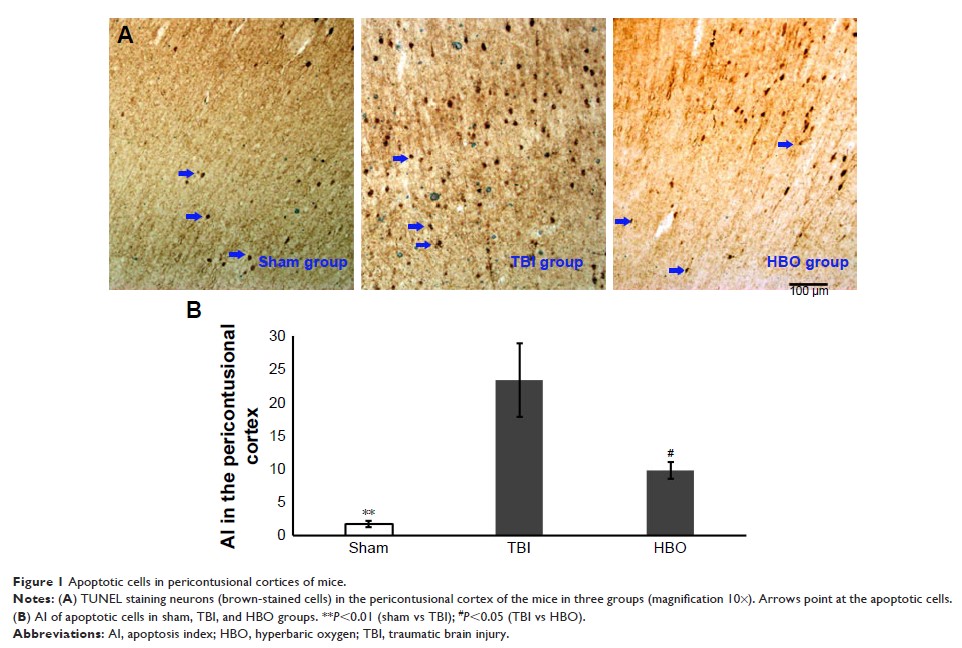
Results: Results
showed that acute TBI increased the number of apoptotic neurons and mRNA
expression and activated caspase 3 protein. With regard to proteins, acute TBI
also resulted in decreased levels of pAkt/Akt, pGSK3β/GSK3β, and β-catenin,
which facilitates neuronal apoptosis. This study shows that HBO therapy
reversed these changes of pAkt/Akt, pGSK3β/GSK3β, and β-catenin induced by
acute TBI and attenuated the apoptotic process in the pericontusional cortex.
Conclusion: This
study demonstrates the beneficial effect of HBO therapy on neuronal apoptosis
caused by acute TBI. Furthermore, the mechanism underlying the therapeutic
effect of HBO on acute TBI partly involves the Akt/GSK3β/β-catenin pathway.
Keywords: hyperbaric
oxygen, TBI, apoptosis, Akt, GSK3β, β-catenin