110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

CENPK 的下调通过调节 YAP1 抑制肝细胞癌的恶性进展
Authors Wang J, Li H, Xia C, Yang X, Dai B, Tao K, Dou K
Received 8 October 2018
Accepted for publication 18 December 2018
Published 29 January 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 869—882
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S190061
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr William Cho
Background: Several
studies have found that centromere protein K (CENPK) is overexpressed in
several tumour types and promotes tumor progression. However, there has been
little research on the role of CENPK in the progression of hepatocellular
carcinoma (HCC).
Materials and methods: The
expression of CENPK in HCC tissues was quantified by Western blot and
quantitative real-time PCR. Cells were transfected with lentiviral plasmids
containing shRNA sequences targeting CENPK and YAP1 to silence the expression
of CENPK and YAP1. Cell Counting Kit-8 assay, colony formation assay, wound
healing assay, and transwell invasion assay were performed to evaluate cell
growth, migration, and invasion of HCC cells. Tumorigenicity assay was used to
detect the effect of CENPK on the growth of HCC cells. Western blot assay was
performed to investigate the expression of epithelial–mesenchymal transition
(EMT) markers and YAP1.
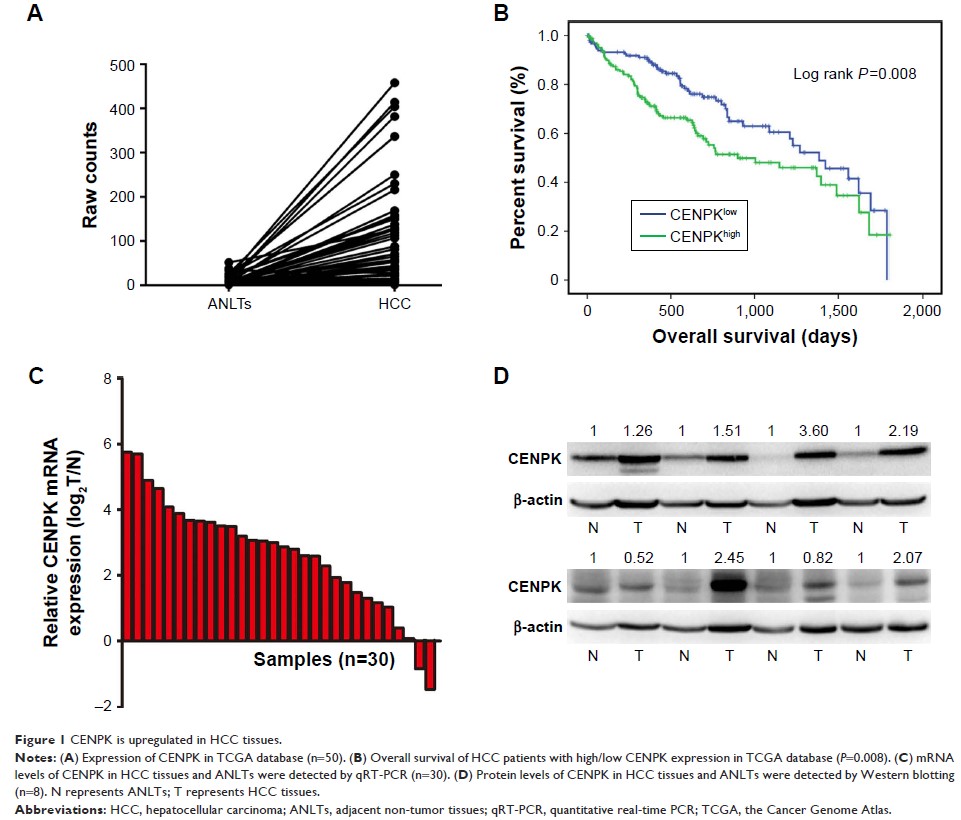
Results: Compared
to that in adjacent non-tumor tissues, CENPK was aberrantly upregulated in HCC
tumor tissues. Furthermore, CENPK knockdown significantly inhibited
proliferation, migration, invasion, and EMT progression in HCC cells.
Mechanistically, we identified that YAP1 was responsible for the tumor-suppressive
effects of CENPK knockdown in the HCC cells. The inhibitory effects of CENPK
silencing on cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and EMT were partially
reversed by the restoration of YAP1 expression.
Conclusion: Our
results suggested that the CENPK–YAP1–EMT axis plays a critical role in
regulating HCC malignant progression, indicating the role of this axis as a
potential therapeutic target for HCC.
Keywords: CENPK,
YAP1, proliferation, migration and invasion, EMT, HCC