110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

隐丹参酮通过抑制 STAT3 活化在体外和体内遏制食管鳞状细胞癌
Authors Ji Y, Liu Y, Xue N, Du T, Wang L, Huang R, Li L, Yan C, Chen X
Received 16 September 2018
Accepted for publication 3 January 2019
Published 29 January 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 883—896
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S187777
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Jianmin Xu
Purpose: Esophageal
squamous-cell carcinoma (ESCC) is the most common subtype of esophageal cancer,
with a poor clinical outcome. Cryptotanshinone (CTS) is the main bioactive
compound from the root of Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge. Our study aimed to
investigate the anti-cancer effects and molecular mechanisms of CTS on ESCC.
Materials and methods: We
investigated the anti-tumor activity of CTS on ESCC in vitro and in vivo.
Activation of the STAT3 signaling pathway was evaluated in ESCC and HEK-Blue™
IL-6 cells. Cell viability was assessed by the MTT assay. Apoptosis and cell
cycle arrest were assessed using flow cytometry. Cell migration was detected by
a scratch wound assay.
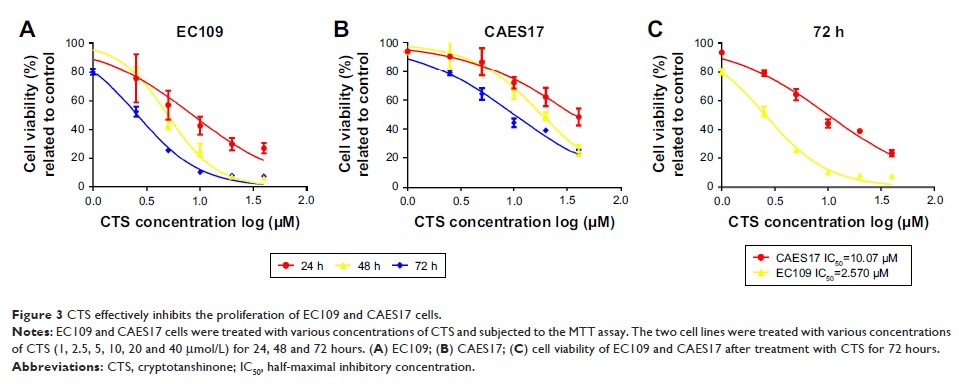
Results: CTS
inhibited STAT3 expression and IL-6-mediated STAT3 activation in esophageal
cancer cells. Subsequently, CTS dose-dependently inhibited the proliferation of
esophageal cancer cells via induction of cell apoptosis. Furthermore, CTS
suppressed the migration of esophageal cancer cells. In vivo, CTS inhibited
tumor growth of EC109 cell in xenograft mice without any obvious effect on body
weight.
Conclusion: Our
results indicated that STAT3 inhibition may be a therapeutic target for
esophageal cancer. CTS could provide a potential approach for esophageal cancer
therapy by influencing the janus kinase-2/STAT3 signaling pathway.
Keywords: xenograft,
CTS, ESCC, proliferation, apoptosis, migration