110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

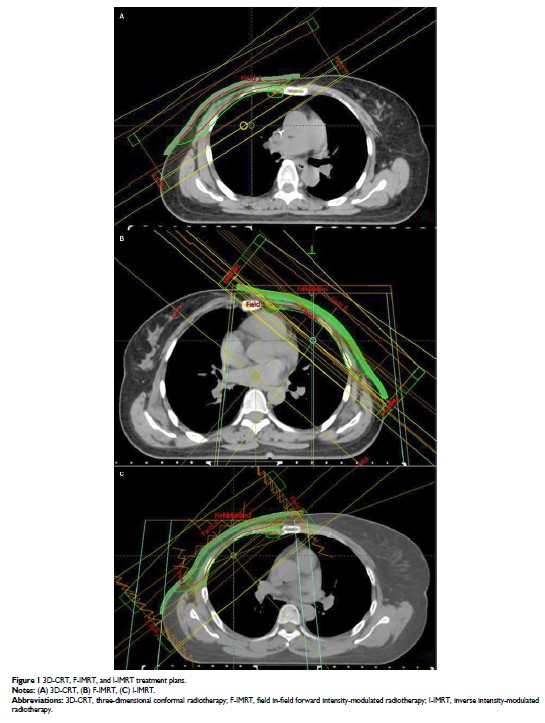
使用三种不同技术的乳房切除术后放疗:内乳淋巴结中偶然剂量分布的回顾性评估
Authors Wang W, Zhang Y, Xu M, Shao Q, Sun T, Yu T, Liu X, Li J
Received 16 October 2018
Accepted for publication 27 December 2018
Published 30 January 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 1097—1106
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S191047
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonella D'Anneo
Objective: To
evaluate the incidental coverage dose to the internal mammary nodes (IMN) in
patients treated with postmastectomy radiotherapy (PMRT) and its relationship
with the treatment plan.
Patients and methods: We
retrospectively analyzed 138 patients undergoing PMRT and divided them into
three groups: three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy (3D-CRT), field-in-field
forward intensity-modulated radiotherapy (F-IMRT), and inverse
intensity-modulated radiotherapy (I-IMRT). The IMN were contoured according to
the Radiation Therapy Oncology Group consensus and not included in the planning
target volume. We analyzed incidental IMN dose coverage and its relationship
with the lung and heart.
Results: The mean
dose (Dmean) to the IMN was 32.85 Gy for all patients, and the dose delivered
to the IMN showed no differences in 3D-CRT, F-IMRT, and I-IMRT (33.80, 29.65,
and 32.95 Gy, respectively). In addition, 10.42%, 2.04%, and 9.76% of patients
achieved ≥45 Gy with 3D-CRT, F-IMRT, and I-IMRT, respectively. No
differences were evident among the three treatment plans regarding IMN dose in
the first three intercostal spaces (ICS1–3). The Dmean, V20, V30, V40, and V50
of ICS2 and ICS3 were superior to those of ICS1 for all three plans. For
3D-CRT, a moderate positive correlation was evident between the Dmean to the
IMN and the Dmean to the heart. For F-IMRT and I-IMRT, positive correlations
were evident between the Dmean of the IMN and the Dmean and V20 of the lung.
Conclusion: The mean
incidental dose to the IMN for IMRT (F-IMRT and I-IMRT) and 3D-CRT after
modified radical mastectomy was insufficient to treat subclinical disease. A
substantial dose was delivered to the IMN in some patients. Higher incidental
doses to the IMN were associated with a higher heart mean dose for 3D-CRT and a
higher dose to the lung for IMRT. Future prospective studies should further
explore subgroups that do not require IMN irradiation.
Keywords: postmastectomy
radiotherapy, internal mammary chain incidental irradiation dose,
three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy, field-in-field forward
intensity-modulated radiotherapy, inverse IMRT