110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

在腰椎间盘突出症大鼠脊髓中新型 lnc RNA 的表征
Authors Wang Q, Ai H, Liu J, Xu M, Zhou Z, Qian C, Xie Y, Yan J
Received 4 February 2018
Accepted for publication 12 December 2018
Published 30 January 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 501—512
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S164604
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Michael Ueberall
Background: Radicular
pain, caused by a lesion or autologous nucleus pulposus (NP) implantation, is
associated with alteration in gene expression of the pain-signaling pathways.
lncRNAs have been shown to play critical roles in neuropathic pain. However,
the mechanistic function of lncRNAs in lumbar disc herniation (LDH) remains
largely unknown. Identifying different lncRNA expression under sham and
NP-implantation conditions in the spinal cord is important for understanding
the molecular mechanisms of radicular pain.
Methods: LDH was
induced by implantation of autologous nucleus pulposus (NP), harvested from rat
tail, in lumbar 5 and 6 spinal nerve roots. The mRNA and lncRNA microarray
analyses demonstrated that the expression profiles of lncRNAs and mRNAs between
the LDH and sham groups were markedly altered at 7 days post operation. The
expression patterns of several mRNAs and lncRNAs were further proved by qPCR.
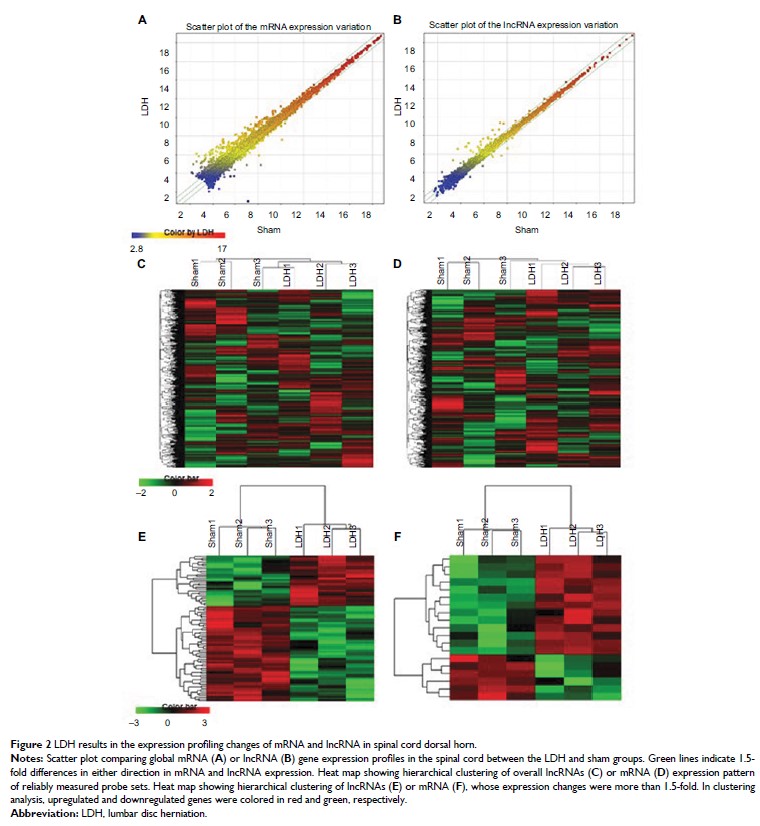
Results: LDH
produced persistent mechanical and thermal hyperalgesia. A total of 19 lncRNAs
was differentially expressed (>1.5-folds), of which 13 was upregulated and 6
was downregulated. In addition, a total of 103 mRNAs was markedly altered
(>1.5-folds), of which 40 was upregulated and 63 downregulated. Biological
analyses of these mRNAs further demonstrated that the most significantly
upregulated genes in LDH included chemotaxis, immune response, and positive
regulation of inflammatory responses, which might be important mechanisms
underlying radicular neuropathic pain. These 19 differentially expressed
lncRNAs have overlapping mRNAs in the genome, which are related to
glutamatergic synapse, cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction, and the
oxytocin-signalling pathway.
Conclusion: Our
findings revealed the alteration of expression patterns of mRNAs and lncRNAs in
the spinal cord of rats in a radicular pain model of LDH. These mRNAs and
lncRNAs might be potential therapeutic targets for the treatment of radicular
pain.
Keywords: lumbar
disc herniation, spinal cord, radicular pain, lncRNA