110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

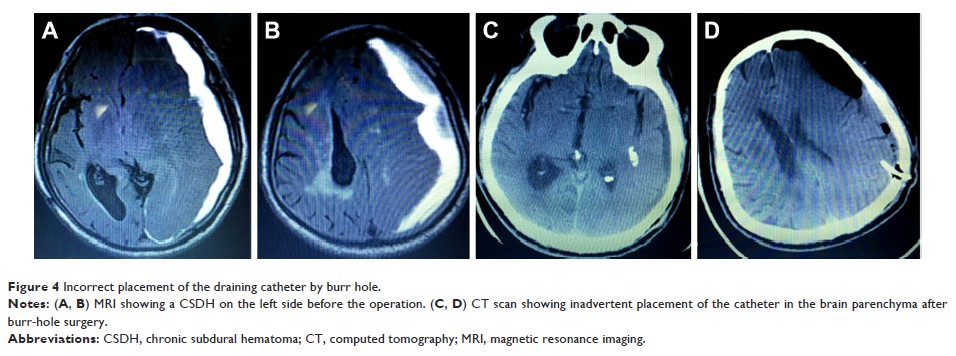
通过经颅神经内窥镜方法疏散慢性和亚急性硬膜下血肿
Authors Cai Q, Guo Q, Zhang F, Sun D, Zhang W, Ji B, Chen Z, Mao S
Received 6 November 2018
Accepted for publication 28 December 2018
Published 30 January 2019 Volume 2019:15 Pages 385—390
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S193548
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yu-Ping Ning
Objective: To evaluate the effectiveness and safety
of neuroendoscopic surgery for chronic or subacute subdural hematoma.
Patients and
methods: Between
September 2016 and September 2018, neuroendoscopic surgery was performed on 25
patients with chronic and subacute subdural hematoma. Hematoma evacuation was performed
with a 0°, 4 mm diameter rigid neuroendoscope via a transcranial
neuroendoscopic approach.
Results: All patients successfully underwent
neuroendoscopic surgery, and no surgical complications or rebleeding was
observed. Postoperative computed tomography scans showed that the hematoma was
successfully evacuated. All patients had recovered well at discharge, the
observed 30-day mortality rate was 0%, and no patients suffered recurrence for
2–26 months after surgery.
Conclusion: Neuroendoscopic surgery was a safe and
effective approach for the treatment of chronic and subacute subdural hematoma.
This approach has the advantages of decent visualization and minimal
invasiveness and could reduce recurrence and the mortality rate.
Keywords: subacute subdural hematoma, chronic
subdural hematoma, transcranial neuroendoscopic approach