110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

miR-135a 通过靶向 TRAF5 介导的 NF-κB 活化来抑制胃癌细胞的迁移
Authors Xie Y, Li F, Li Z, Shi Z
Received 6 October 2018
Accepted for publication 8 January 2019
Published 1 February 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 975—984
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S189976
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Geoffrey Pietersz
Background: As
crucial regulators and possible biomarkers for cancer development, miRNAs have
attracted intensive attention during the last two decades. Among the known
miRNAs, miR-135a has been indicated as a tumor suppressor in several cancer
types, whereas its roles and mechanisms in gastric cancer (GC) remain largely
unclear.
Materials and methods: Quantitative
PCR (qPCR) was conducted to detect the expression of miR-135a in paired GC
tissues as well as cell lines. The prognostic value was evaluated by
Kaplan–Meier survival analysis. Wound healing and transwell assays were
performed to determine the roles of miR-135a in GC cell migration.
Dual-luciferase reporter assay, qPCR, and Western blot analysis were used to
validate the targeting of TRAF5 and subsequent NF-κB pathway by miR-135a.
Rescue experiments were done to explain the involvement of TRAF5 in mediating
the anti-migration effect of miR-135a in GC cells. Finally, the expression of
TRAF5 was examined in paired GC tissues.
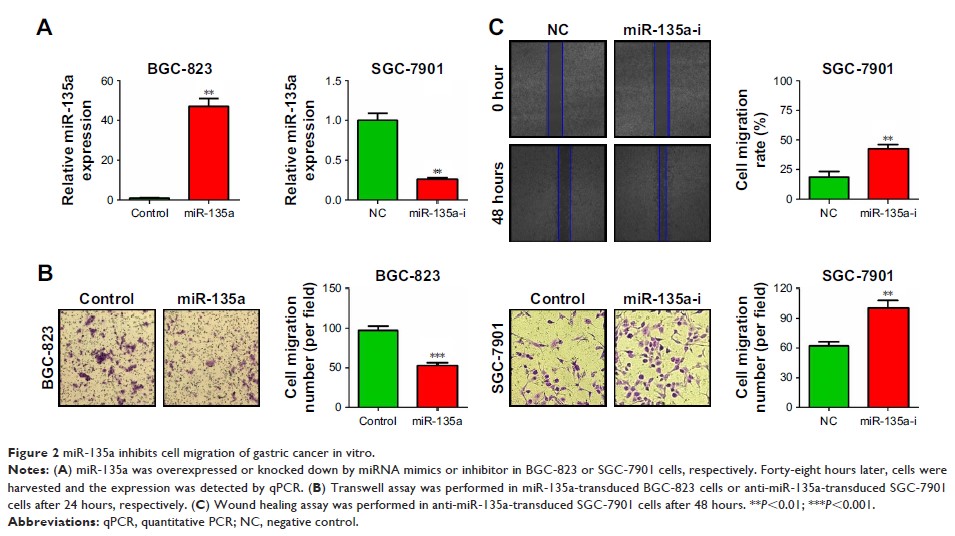
Results: miR-135a
was confirmed to be decreased in GC tissues and cell lines, and its lower
expression predicted worse overall survival. Cellular experiments proved that
miR-135a suppressed migration in GC cells. Through directly targeting TRAF5 and
subsequently inhibiting NF-κB pathway, miR-135a might efficiently inhibit GC
cell metastasis. Furthermore, we found that TRAF5 overexpression was negatively
correlated with miR-135a expression in GC tissues.
Conclusion: Our study
indicated that miR-135a serves a suppressing role in GC cell migration by
targeting TRAF5 and the downstream NF-κB pathway.
Keywords: miR-135a,
gastric cancer, TRAF5, NF-κB pathway, cell migration