111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

针对 AGS 胃癌细胞应用倒地鈴,研究生物方式合成的金纳米粒的细胞毒性及胱天蛋白酶介导的细胞凋亡作用
Authors Li C, Wang Y, Zhang H, Li M, Zhu Z, Xue Y
Received 1 November 2018
Accepted for publication 14 December 2018
Published 5 February 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 951—962
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S193064
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Background: Gastric
cancer is the fourth most common cancer and second leading cause of cancer
death worldwide. Cardiospermum halicacabum is used to treat nerve
disorders, stiffness, rheumatism, ear ache, snake bite, and so on.
Methods: In this
study, the reaction parameters were optimized to control the size of the
nanoparticle, which was confirmed by transmission electron microscopy. Various
characterization techniques such as selected area diffraction pattern,
UV-visible spectroscopy, energy-dispersive X-ray analysis, dynamic light scattering,
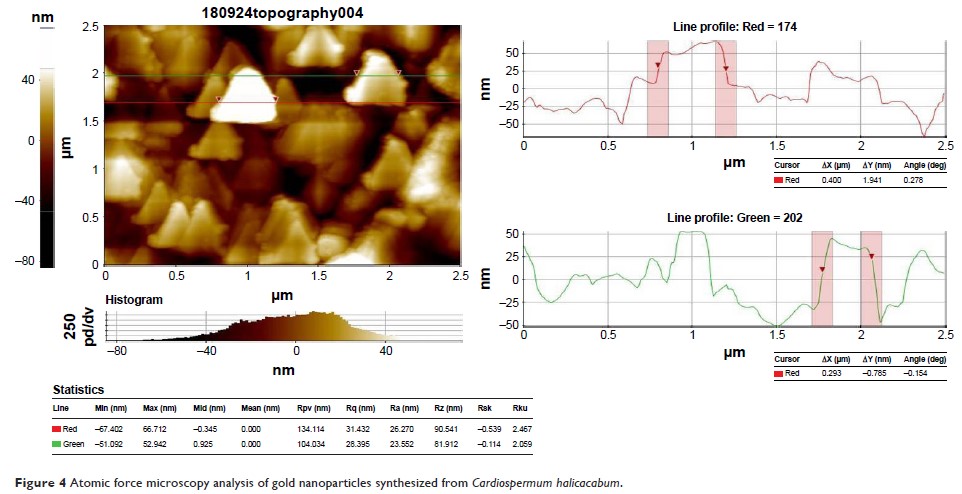
Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy, and atomic force microscopy were
employed to analyze the synthesized AuNPs obtained from C. halicacabum (CH-AuNP)
against gastric carcinoma cell line.
Results: The
cytotoxic effect of CH-AuNP against AGS, SNU-5, and SNU-16 cell lines was
detected by MTT assay. The induction of apoptosis by CH-AuNP in AGS was
analyzed by double staining technique using TUNEL and DAPI staining assays.
Further to confirm the molecular mechanism exhibited by CH-AuNP to induce apoptosis,
the intracellular ROS level was assessed and immunoblotting was performed to
assess the apoptotic signaling molecules that often deregulated in cancerous
condition.
Conclusion: The results
clearly prove that CH-AuNP increases ROS and induces apoptosis in AGS,
suggesting that CH-AuNP may be an effective anticancer drug with no side
effects to treat gastric cancer.
Keywords: gastric
cancer, gold nanoparticle Cardiospermum halicacabum , apoptosis, MMP, ROS