111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

银杏叶提取物-761 通过调节 Akt/Nrf2 信号通路保护心肌
Authors Chen X, Ren S, Dong J, Qiu C, Chen Y, Tao H
Received 19 October 2018
Accepted for publication 24 December 2018
Published 13 February 2019 Volume 2019:13 Pages 647—655
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S191537
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Anastasios Lymperopoulos
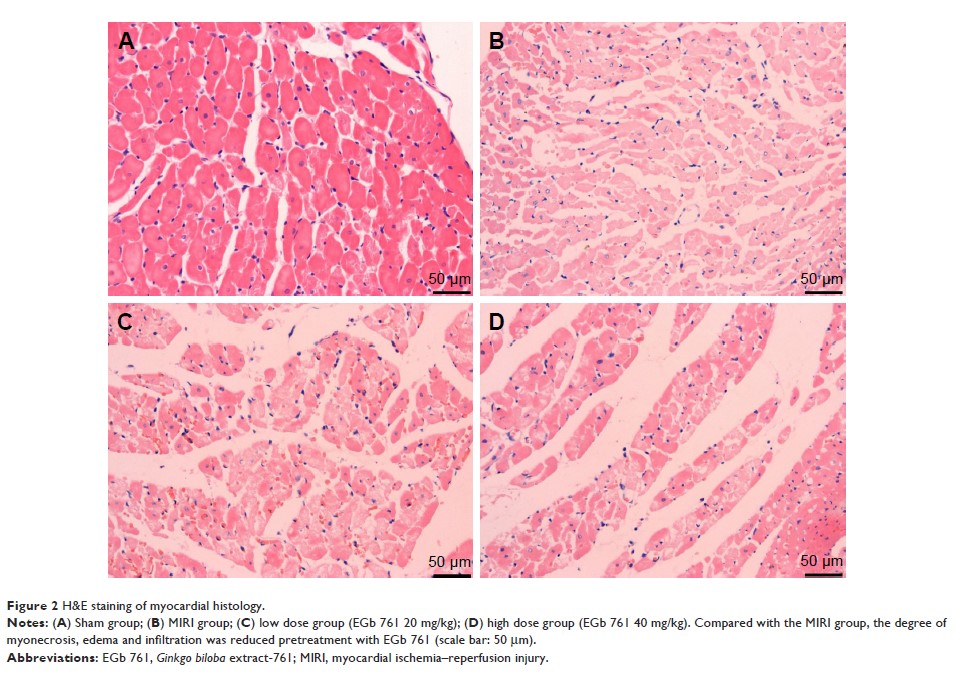
Objective: The aim
of this study was to investigate the protective effect and mechanism of Ginkgo
biloba extract-761 (EGb 761) in the rat with myocardial ischemia–reperfusion
injury (MIRI).
Materials and methods: Forty
Sprague Dawley rats were randomly divided into following four groups: sham
group, I/R group and EGb 761 groups (20 and 40 mg/kg). MIRI model was
established after 14 days of administration. The myocardial infarct size and
myocardial histology were measured and compared. Meanwhile, the levels of
creatine kinase-MB (CK-MB), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), troponin T (TnT),
TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, superoxide dismutase (SOD), malondialdehyde (MDA) and
glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) were evaluated. Western blot was used to detect
the expression of Caspase-3, Bax, Bcl-2, HO-1, Nrf2, Akt, p-Akt and nuclear
protein Nrf2.
Results: The
levels of infarct size, CK-MB, LDH, TnT, TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β in the EGb 761
groups were significantly lower than those in the ischemia/reperfusion (I/R)
group. The content of MDA was lower in the myocardium, whereas the activities
of SOD and GSH-Px were higher than those in the I/R group. The expressions of
Caspase-3 and Bax in the EGb 761 groups were significantly lower than those in
the I/R group, whereas the expressions of Bcl-2, p-Akt and HO-1 and nuclear
protein Nrf2 in the EGb 761 groups were higher than those in the I/R group.
Conclusion: EGb 761
might inhibit the apoptosis of myocardial cells and protect the myocardium by
activating the Akt/Nrf2 pathway, increasing the expression of HO-1, decreasing
oxidative stress and repressing inflammatory reaction.
Keywords: Ginkgo biloba extract,
myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury, oxidative stress, superoxide dismutase