111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

关节内注射透明质酸-青藤碱轭合物治疗骨关节炎的药代动力学和药效学评价
Authors Liu J, Shao H, Fang S, Cheng Y, Ling P, Chen J
Received 5 September 2018
Accepted for publication 28 December 2018
Published 15 February 2019 Volume 2019:13 Pages 657—665
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S186558
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sukesh Voruganti
Objectives: Intra-articular
injection of sinomenine (SN) is an effective treatment method for knee
osteoarthritis (OA), however, SN could be eliminated quickly in vivo. To
extend the residence time of SN in the joint cavity, the SN-hyaluronic acid
(HA) conjugate was prepared previously. This study was performed to evaluate
the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of SN-HA conjugate after
intra-articular administration for the treatment of OA.
Methods: A high
performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS/MS) method was
established to determine the SN content in rat synovial fluid. One hundred and
twenty rats were randomly divided into two groups, the SN-HA group and SN
group. The concentration of SN in articular cavity washings was determined by
HPLC-MS/MS. The protective effect on the cartilage was evaluated by
histological evaluation in a model of papain induced rabbit knee
osteoarthritis.
Results: The
method was validated with respect to sensitivity, specificity, linearity,
precision, accuracy and especially the stability of analytes under various
conditions, and was successfully applied in evaluating the pharmacokinetic
profiles of SN in the joint cavity. Compared to the SN injection, the drug
exposure in joint cavity was significantly increased following SN-HA injection
administration, and AUC(0–12h) was 2.9
times of SN injection, mean residence time (MRT) was 1.88 times of SN
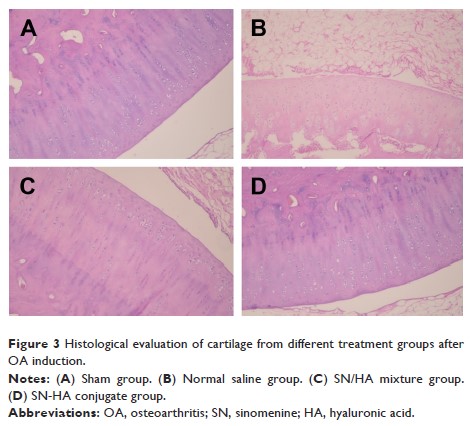
injection. In the pharmacodynamic study, there was no significant difference
between the SN-HA twice-treated group and SH/HA five-times mixture-treated
group.
Conclusion: The local
bioavailability of SN in joint cavity was improved significantly after
conjugated with HA. The SN-HA conjugate showed good synergism effect of OA
inhibition. The results indicated that the SN-HA conjugate seemed to be an
effective therapeutic means for the treatment of OA.
Keywords: sinomenine-hyaluronic
acid conjugate, HPLC-MS/MS, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, osteoarthritis