111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

miR-140-5p 通过直接靶向 TGFBR1 基因减缓了 Wilms 肿瘤的侵袭性进展
Received 17 June 2018
Accepted for publication 4 January 2019
Published 19 February 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 1641—1651
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S177508
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Kenan Onel
Background and objective: Although
many miRNAs are identified to be deregulated and play vital roles in the
progression of Wilms’ tumor (WT), there are still a large number of miRNAs are
waiting for us to explore. The purpose of the present study is to investigate
the different expressing profiles of miRNAs in WT tissues and the adjacent
normal tissues, and probe the effects and mechanism of a certain miRNA among
the different expressing miRNAs.
Methods: miRNA
microarray was recruited to assess the differently expressed miRNAs in WT
tissues and normal tissues, which was further verified by RT-PCR. Receiver
operating characteristic curves were performed to calculate the specificity and
sensitivity of miRNAs in the diagnose of WT. CCK-8, flow cytometry, wound
healing, transwell chamber and tumor-burdened assays were used to assess cell
growth, apoptosis, migration, invasion and tumorigenesis. Luciferase report
assay was used to evaluate the interaction between miR-140-5p and TGFBR1 .
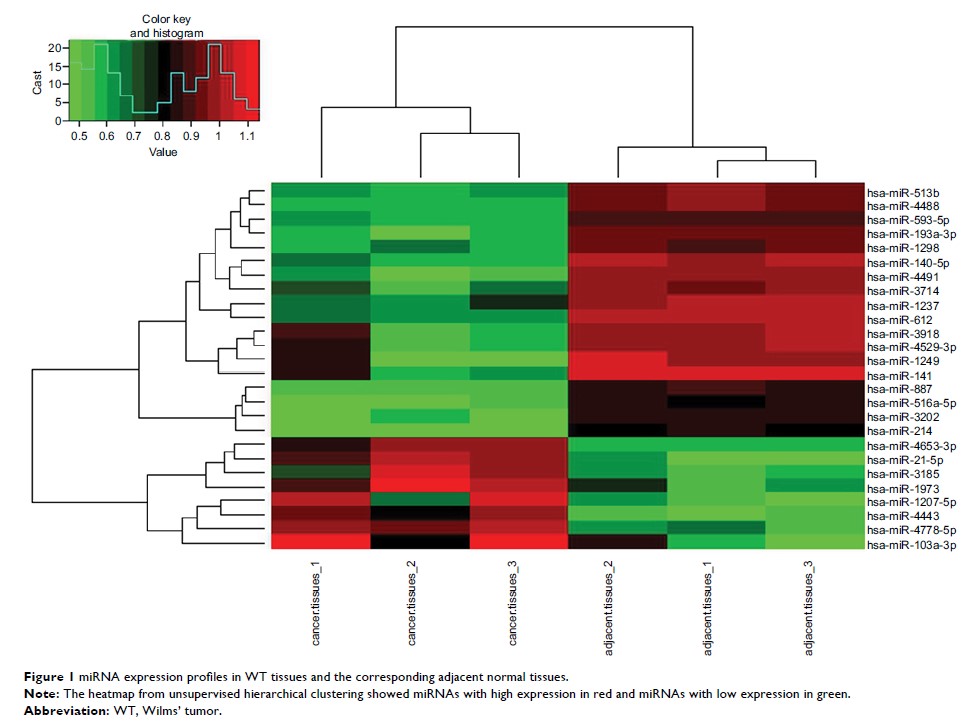
Results: A total
of 34 miRNAs were abnormally expressed in the WT tissues, among which,
miR-140-5p was identified to be obviously down-regulated in WT tissues, and the
AUC of it was 0.961. Besides, we found that patients with miR-140-5p low
expression always had a shorter overall survival and more aggressive clinical
features, such as bigger tumor size (P =0.002), higher pathological stage (P =0.003) and higher
occurrence rate of lymph node metastasis (P =0.009) than those in patients with miR-140-5p high
expression. Moreover, luciferase reporter assay showed that TGFBR1 was the
direct target of miR-140-5p, which was negatively regulated by miR-140-5p and
was highly expressed in WT tissues. Furthermore, knockdown of miR-140-5p
obviously enhanced the proliferation and tumorigenesis and repressed the
apoptosis of G401 cells, and these effects were all abolished when TGFBR1 was
down-regulated.
Conclusion: The
present study illustrates that miR-140-5p functions as a tumor suppressor in
the occurrence and development of WT via targeting TGFBR1 , which
provides theoretical foundation for serving miR-140-5p as a new diagnosis
marker even a therapeutic target for WT.
Keywords: miR-140-5p, TGFBR1 , Wilms’
tumor