111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

脂质纳米气泡作为超声触发的青蒿琥酯传递系统,用于成像引导的肿瘤靶向化学疗法
Authors Gao S, Cheng X, Li J
Received 10 October 2018
Accepted for publication 4 December 2018
Published 6 March 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 1841—1850
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S190208
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Takuya Aoki
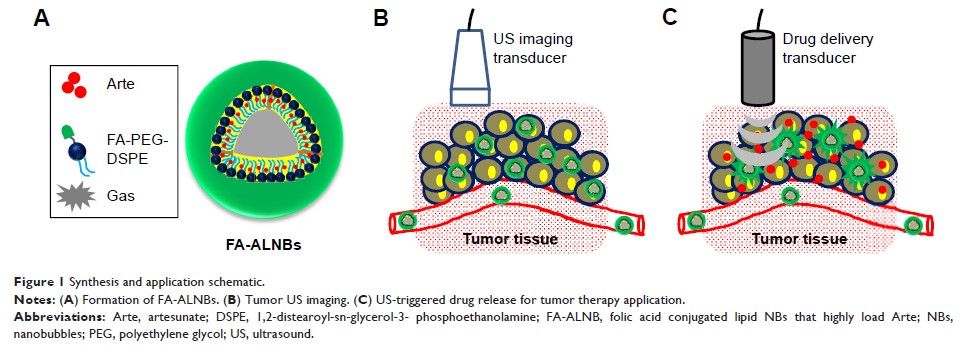
Purpose: Herein,
this study is to prepare folic acid (FA)-conjugated lipid nanobubbles (NBs)
that highly load artesunate (Arte; FA-ALNBs), as an ultrasound (US)-triggered
Arte delivery system for imaging-guided, tumor-targeted chemotherapy.
Materials and methods: The
morphology, size, zeta potential, and stability of the FA-ALNBs were detected
by optical microscopy and dynamic light scattering analysis. The cellular
uptake of the FA-ALNBs was evaluated by confocal laser scanning microscopy and
flow cytometry.
Results: The
FA-ALNBs showed uniform spheroidal structure, with 781.2±5.3 nm in average
diameter, great physiological stability, and ~91.9%±1.1% encapsulation
efficiency of Arte. Using focused US, about 36.1%±2.5% of the entrapped Arte
was trigger-released from the FA-ALNBs. Owing to the US contrast property,
FA-ALNBs showed an enhanced US signal in vitro when using an ultrasonic
diagnostic apparatus with a 1-MHz linear transducer. Due to the FA
receptor-mediated endocytosis effect, FA-ALNBs can be efficiently internalized
by cells, showing an uptake ratio of about 56.4%±3.1%. FA-ALNBs showed an
enhanced, dose-dependent cell-killing ability, while FA-ALNBs plus US
irradiation exhibited a stronger anticancer effect in vitro. Post intravenous
injection into tumor-bearing mice, FA-ALNBs showed an enhanced US contrast
effect with increase in time, indicating the increasing accumulation of
FA-ALNBs in tumor tissue, which peaked at 4 hours post injection. Focused US
irradiation was conducted on the tumor region at 4 hours post injection of
FA-ALNBs, which showed a greater tumor suppression effect after 30 days of
treatment compared with all other treatment groups. Moreover, FA-ALNBs showed
negligible systemic toxicity in vivo.
Conclusion: This
versatile US-triggered drug delivery system with great anticancer efficacy was
assessed both in vitro and in vivo, revealing great potential as a cancer
theranostic agent for future application.
Keywords: nanobubbles,
artesunate, ultrasound imaging, ultrasound-triggered drug release, cancer
theranostics