111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

使用掺杂氧化石墨烯的静电纺丝聚乳酸-乙醇酸载药纳米纤维膜促进肌腱与骨整合
Authors Su W, Wang Z, Jiang J, Liu X, Zhao J, Zhang Z
Received 14 August 2018
Accepted for publication 8 February 2019
Published 11 March 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 1835—1847
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S183842
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Thomas Webster
Background: These
normal entheses are not reestablished after repair despite significant advances
in surgical techniques. There is a significant need to develop integrative
biomaterials, facilitating functional tendon-to-bone integration.
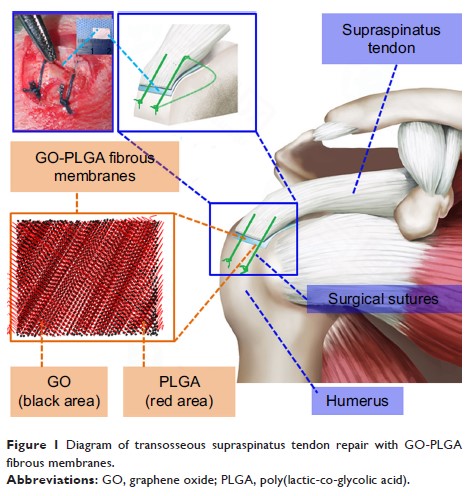
Materials and methods: We
fabricated a highly interconnective graphene oxide-doped electrospun
poly(lactide-co-glycolide acid) (GO-PLGA) nanofibrous membrane by
electrospinning technique and evaluated them using in vitro cell assays. Then,
we established rabbit models, the PLGA and GO-PLGA nanofibrous membranes were
used to augment the rotator cuff repairs. The animals were killed
postoperatively, which was followed by micro-computed tomography, histological
and biomechanical evaluation.
Results: GO was
easily mixed into PLGA filament without changing the three dimensional
microstructure. An in vitro evaluation demonstrated that the PLGA membranes
incorporated with GO accelerated the proliferation of BMSCs and furthered the
Osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs. In addition, an in vivo assessment further
revealed that the local application of GO-PLGA membrane to the gap between the
tendon and the bone in a rabbit model promoted the healing enthesis, increased
new bone and cartilage generation, and improved collagen arrangement and
biomechanical properties in comparison with repair with PLGA only.
Conclusion: The
electrospun GO-PLGA fibrous membrane provides an effective approach for the
regeneration of tendon to bone enthesis.
Keywords: enthesis,
osteogenic material, cartilage, collagen arrangement, rabbit model