111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

中国疾控中心为了控制中国传染病和地方病而提供的公共卫生服务的系统动力学模型
Authors Li M, Yu W, Tian W, Ge Y, Liu Y, Ding T, Zhang L
Received 24 August 2018
Accepted for publication 29 January 2019
Published 13 March 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 613—625
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IDR.S185177
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Joachim Wink
Background: Infectious
and endemic diseases are a serious public health concern worldwide, and their
prevention and treatment are globally controversial. This study aimed to
establish an system dynamics (SD) model to analyze the factors influencing
public health services provided by the Chinese Centers for Disease Control and
Prevention (China CDC) to implement infectious and endemic disease control in
China, by establishing more effective interventions to provide public health
services and thus achieving the goal of controlling infectious and endemic
diseases.
Materials and methods: An SD
model was constructed using the Vensim DSS program. Intervention experiments
were performed using the SD model, which reflected the influences on disease
control by adjusting the governmental investment and compensation level for
public health products.
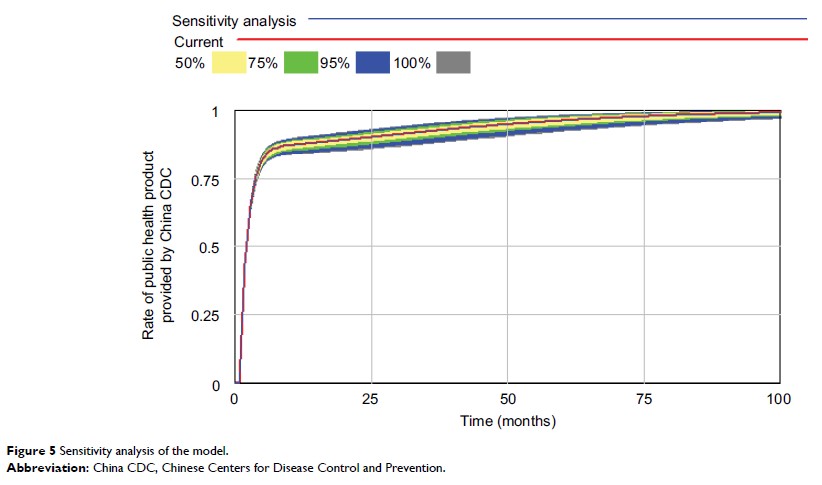
Results: The
experimental results showed that increasing the governmental investment in
China CDC and compensation level for public health products will significantly
increase the public health product rate provided by China CDC.
Discussion: Problems with
infectious and endemic disease prevention and treatment are the result of the
system’s incomplete functioning and limited health resources. To address the
current problems and improve the system, the government should increase its
investment in the public health service system and improve the compensation
system to ensure smooth implementation of infectious and endemic disease
prevention and treatment and, ultimately, improve public health in China.
Keywords: epidemic
model, transmission, spread, epidemiology, public health, system dynamics,
disease management