111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

移植前代谢综合征及其组成可预测接受第一次肾移植的中国患者的移植后糖尿病
Authors Cai R, Wu M, Xing YF
Received 8 October 2018
Accepted for publication 25 January 2019
Published 14 March 2019 Volume 2019:15 Pages 497—503
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/TCRM.S190185
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Deyun Wang
Background: Post-transplantation
diabetes mellitus (PTDM) remains a major clinical challenge following renal
transplant. Identification of pretransplant modifiable risk factors may allow
timely interventions to prevent PTDM. This study aims to determine whether
pretransplant metabolic syndrome and its components are able to predict PTDM in
Chinese patients receiving their first renal transplant.
Patients and methods: We
conducted a single-center retrospective study of 633 non-diabetic patients
receiving a first kidney transplant. PTDM was diagnosed between 1 month and 1
year post-transplant. Multivariable logistic regression and Cox proportional
hazards model were applied to detect potential pretransplant risk factors for
PTDM.
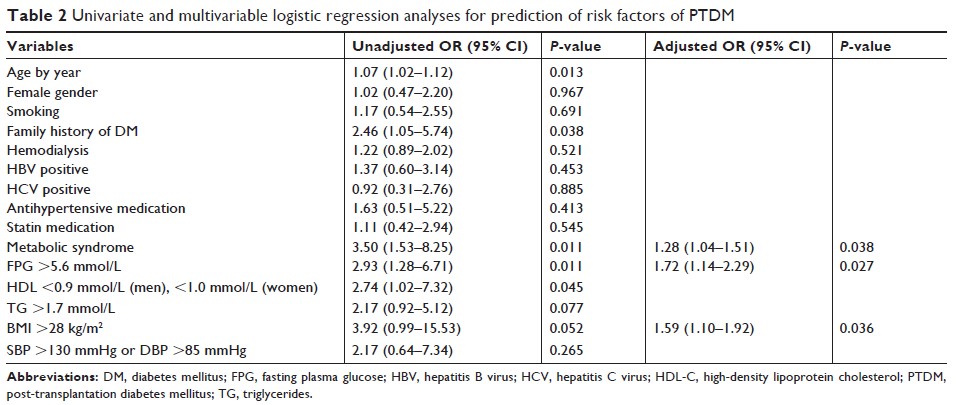
Results: One year
post-transplant, 26.2% of recipients had developed PTDM. PTDM patients had
significantly higher fasting plasma glucose (FPG) (P =0.026) and body
mass index (BMI) (P =0.006) than non-PRDM patients, and lower levels of
high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (P =0.015). The presence of metabolic syndrome was an
independent risk factor for PTDM, as assessed by multivariable logistic
regression analysis (OR 1.28, 95% CI 1.04–1.51, P =0.038) and Cox
proportional hazards model (OR 2.75, 95% CI 1.45–6.05, P =0.021). Moreover,
both FPG >5.6 mmol/L and BMI >28 kg/m2 (obesity)
were able to predict PTDM.
Conclusion: Our
results suggest that the presence of metabolic syndrome and its components,
impaired fasting glycemia and obesity, are independent risk factors for PTDM in
Chinese non-diabetic patients receiving a first renal transplant. Interventions
aimed at improving pretransplant metabolic syndrome may reduce the incidence of
PTDM.
Keywords: post-transplantation
diabetes mellitus, renal transplant, metabolic syndrome, body mass index,
fasting plasma glucose