111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

基于 β-环糊精的 pH 敏感、载多柔比星的聚合物纳米复合物用于肝癌靶向治疗
Authors Yang T, Du G, Cui Y, Yu R, Hua C, Tian W, Zhang Y
Received 2 November 2018
Accepted for publication 3 February 2019
Published 21 March 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 1997—2010
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S193170
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
Background: Doxorubicin
(DOX) is one of the most effective treatments for hepatocellular carcinoma
(HCC), but is restricted by its poor pharmacokinetics. Herein, we exploited
efficient targeted drug delivery systems and they have been found to be a
worthy strategy for liver cancer therapy.
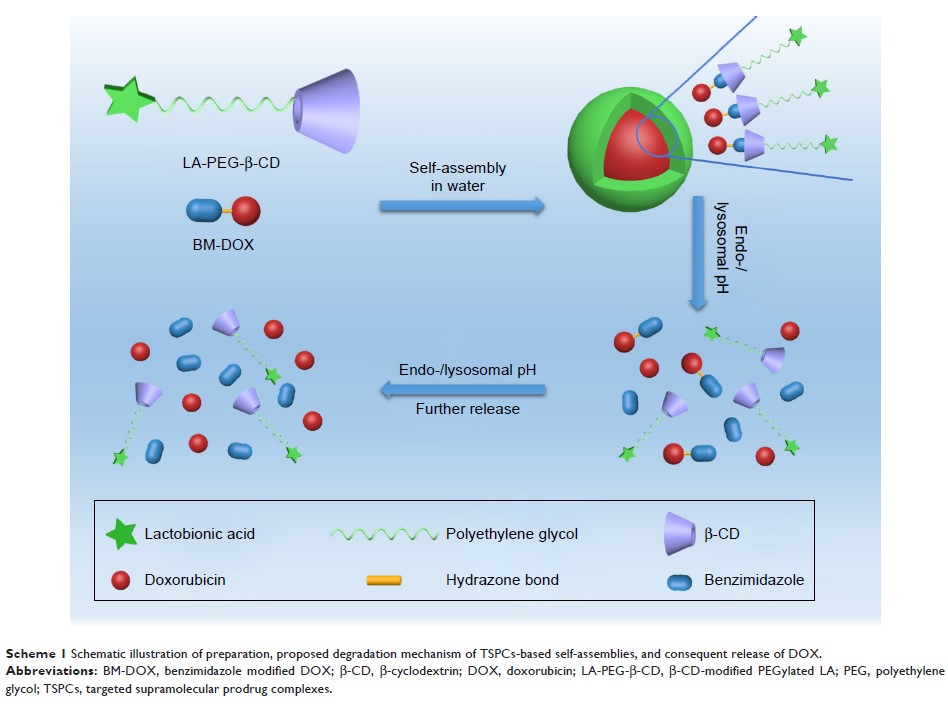
Materials and methods: We
investigated polymeric nanoparticles which were synthesized based on host–guest
interaction between β-cyclodextrin and benzimidazole. The properties of
nanoparticles with regard to size/shape, encapsulation efficiency, and drug release
were investigated using conventional experiments. Cell proliferation assay
in vitro, cell uptake assay, and cell apoptosis analysis were used to
investigate cytotoxicity, uptake, and mechanism of targeted supramolecular
prodrug complexes (TSPCs)-based self-assemblies and supramolecular prodrug
complexes (SPCs)-based self-assemblies.
Results: The
pH-sensitive lactobionic acid (LA)-modified pH-sensitive self-assemblies were
synthesized successfully. The results of in vitro released assay showed that
the accelerated released of DOX from TSPCs-based self-assemblies with the
decrease of pH value. When TSPCs-based self-assemblies were taken up by HepG2
cells, they demonstrated a faster release rate under acidic conditions and
proved to have higher cytotoxicity than in the presence of LA. A mechanistic
study revealed that TSPCs-based self-assemblies inhibited liver cell
proliferation by inducing cell apoptosis.
Conclusion: The
pH-sensitive nanocomplex, as liver-targeted nanoparticles, facilitated the
efficacy of DOX in HepG2 cells, offering an appealing strategy for the
treatment of HCC.
Keywords: pH-sensitive,
hepatocellular carcinoma, doxorubicin, drug delivery