111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

老年人乳头状甲状腺微小癌的临床病理特征和复发风险
Authors Wang X, Lei J, Wei T, Zhu J, Li Z
Received 16 December 2018
Accepted for publication 27 February 2019
Published 25 March 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 2371—2377
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S198451
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonella D'Anneo
Background: The
optimal management for elderly patients with papillary thyroid microcarcinoma
(PTMC) is not well established. The aim of the present study is to describe the
clinicopathological characteristics and identify predictors of recurrence in
the elderly PTMC patients.
Methods: We
conducted a retrospective study of PTMC patients who underwent thyroidectomy.
The clinicopathological characteristics were compared between patients with age
≥65 years and <65 years. The independent predictors of recurrence were
identified by
multivariate Cox regression analysis.
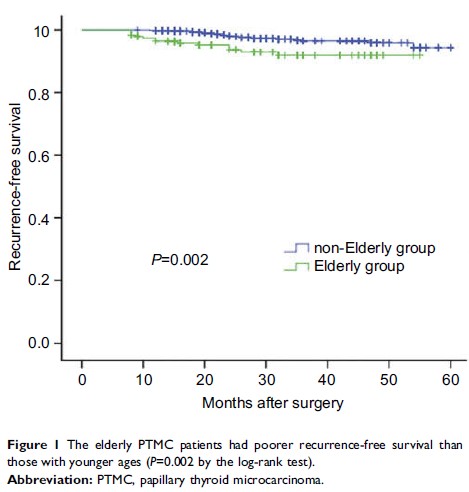
Results: The
patients in elderly group were more likely to exhibit bilaterality (P <0.050),
extrathyroidal extension (P < 0.001), and central compartment lymph node
metastasis (CLNM) (P <0.010), especially the ratio of CLNM >0.5 (P <0.010), than
the patients with age P =0.002). Multivariate analysis indicated tumor size
>5 mm (P =0.009)
and CLNM ratio >0.5 (P =0.002) were independent risk factors for recurrence
of the elderly patients with PTMC.
Conclusions: The
elderly PTMC patients have more aggressive biological characteristics and
higher recurrence rate. More aggressive treatment and rigorous follow-up could
be considered for elderly patients with tumor diameter >5 mm and CLNM ratio
>0.5.
Keywords: papillary
thyroid microcarcinoma, recurrence, elderly