111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

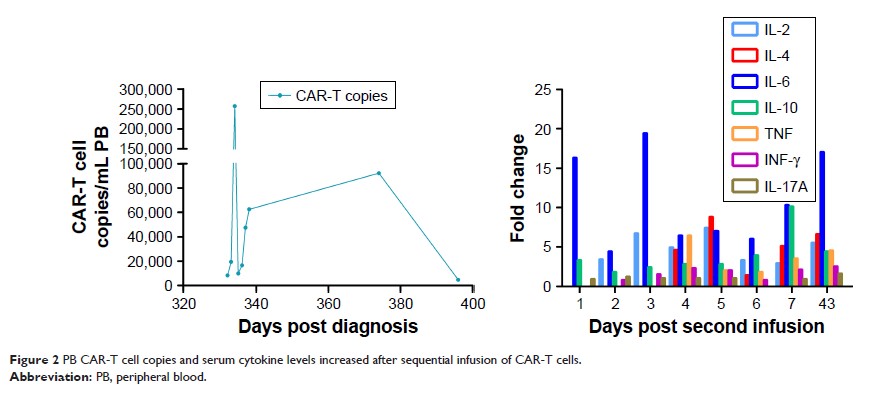
对患有复发/难治性急性淋巴细胞白血病且之前暴露于鼠源性 CD19 特异性 CAR-T 细胞的患者序贯输注人源化 CD19 和 CD22 修饰的 CAR-T 细胞后出现的延迟缓解
Authors Yang F, Zhang J, Zhang X, Tian M, Wang J, Kang L, Qiu H, Wu D
Received 28 September 2018
Accepted for publication 14 February 2019
Published 25 March 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 2187—2191
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S189103
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjay Singh
Background: CD19-modified
CAR-T cells greatly influence responses in patients with relapsed/refractory
acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). However, recurrence remains a challenge,
and reinfusion of CAR-T cells is not always effective. Sequential infusion of
humanized CD19-modified and CD22-modified CAR-T cells may overcome this issue
and induce remission.
Methods: We
examined treatment with sequential infusion of humanized CD19-modified and
CD22-modified CAR-T cells in a patient with relapsed ALL previously exposed to
murine-derived anti-CD19 CAR-T cells.
Results: At
~6 weeks after treatment, repeated bone marrow smear and flow cytometry
analysis revealed no lymphoblasts.
Conclusion: Our
results suggest that sequential infusion of humanized CD19-modified and
CD22-modified CAR-T cells is a valuable option for relapsed patients with prior
infusion of murine-derived, CD19-directed CAR-T cells.
Keywords: chimeric
antigen receptor, anti-CD19, anti-CD22, humanized, acute lymphoblastic
leukemia, relapsed