111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

IRAK1 对接受新辅助化疗治疗的乳腺癌患者的作用
Authors Yang M, Qin X, Qin G, Zheng X
Received 29 August 2018
Accepted for publication 14 January 2019
Published 25 March 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 2171—2180
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S185662
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr William Cho
Background: IRAK1 has
been shown to be abnormally expressed in a set of tumors leading to
tumorigenesis and progression. IRAK1 is a therapeutic target that drives breast
cancer metastasis and resistance to paclitaxel. However, the exact role of
IRAK1 in neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NCT) for breast cancer remains unclear. The
aim of this study was to investigate the relationship between the expression of
IRAK1 and the clinicopathological parameters and survival prognosis of breast
cancer patients treated with NCT.
Patients and methods: Based on
the clinical data and mRNA microarray data from 1,085 breast cancer patients in
The Cancer Genome Atlas, the correlation between IRAK1 expression and
clinicopathological parameters of breast cancer was analyzed.
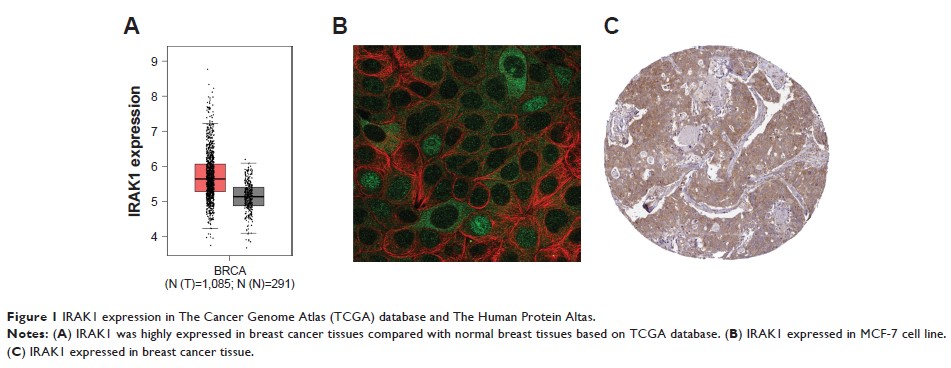
Immunohistochemistry was performed to evaluate the expression of IRAK1. The
Human Protein Atlas and the String database were used to analyze the expression
of IRAK1 protein and its interaction with altered neighboring proteins in
breast cancer. IRAK1 alteration was analyzed in cBioPortal database. GEO
enrichment of IRAK1 was performed using WEB-based Gene SeT AnaLysis Toolkit.
Results: The
expression of IRAK1 was significantly downregulated following NCT. The
decreased expression of IRAK1 following NCT was positively correlated with
reduced tumor size. Finally, survival analysis confirmed that a shorter
survival period was correlated to higher expression of IRAK1 both before and
after NCT.
Conclusion: These
findings advanced our understanding about the expression pattern of IRAK1 in
breast cancer, especially in those patients who were treated with NCT,
suggesting that IRAK1 could be used as a prognostic indicator, as well as a
potential indicator for evaluating NCT efficacy for breast cancer patients.
Keywords: IRAK1,
breast cancer, neoadjuvant chemotherapy, bioinformatics, survival