110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

肝细胞癌患者预后列线图的开发和外部验证:一个基于人口的研究
Authors Xiao Z, Yan Y, Zhou Q, Liu H, Huang P, Zhou Q, Lai C, Zhang J, Wang J, Mao K
Received 18 October 2018
Accepted for publication 25 February 2019
Published 10 April 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 2691—2708
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S191287
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Kenan Onel
Background: We
attempted to construct and validate novel nomograms to predict overall survival
(OS) and cancer-specific survival (CSS) in patients with hepatocellular
carcinoma (HCC).
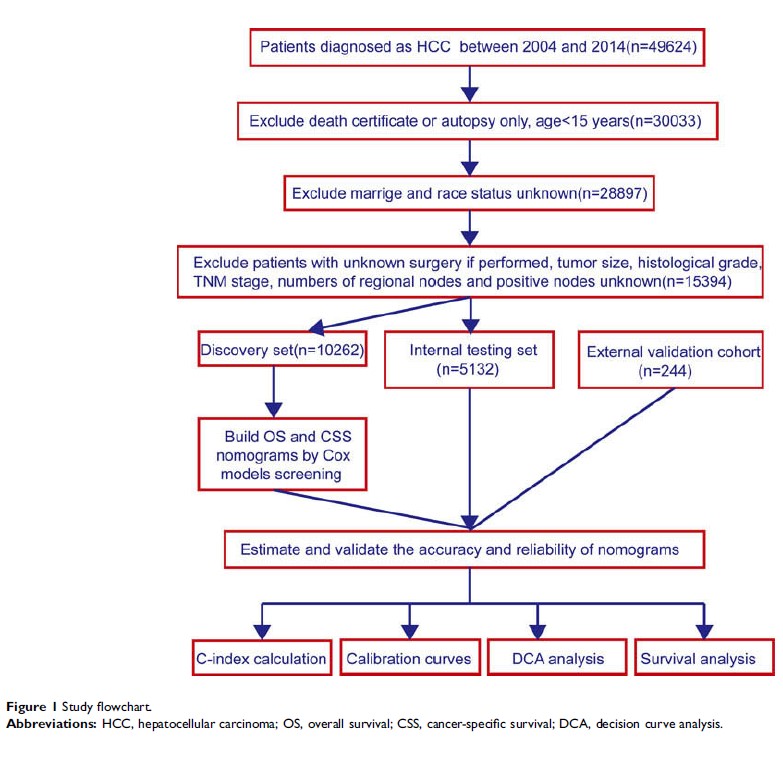
Methods: Models
were established using a discovery set (n=10,262) obtained from the
Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database. Based on
univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses, we identified independent
risk factors for OS and CSS. Concordance indexes (c-indexes) and calibration
plots were used to evaluate model discrimination. The predictive accuracy and
clinical values of the nomograms were measured by decision curve analysis
(DCA).
Results: Our OS
nomogram with a c-index of 0.753 (95% confidence interval (CI), 0.745–0.761)
was based on age, sex, race, marital status, histological grade, TNM stage,
tumor size, and surgery performed, and it performed better than TNM stage. Our
CSS nomogram had a c-index of 0.748 (95% CI, 0.740–0.756). The calibration
curves fit well. DCA showed that the two nomograms provided substantial
clinical value. Internal validation produced c-indexes of 0.758 and 0.752 for
OS and CSS, respectively, while external validation in the Sun Yat-sen Memorial
Hospital (SYMH) cohort produced a c-indexes of 0.702 and 0.686 for OS and CSS,
respectively.
Conclusions: We have
developed nomograms that enable more accurate individualized predictions of OS
and CSS to help doctors better formulate individual treatment and follow-up
management strategies.
Keywords: surveillance,
epidemiology and end results, overall survival, cancer-specific survival,
decision curve analysis