110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

自组装抗血管生成硫酸软骨素-ES2-AF 纳米粒子共轭物的表征和生物活性
Authors Xing L, Sun F, Wang Z, Li Y, Yang Z, Wang F, Zhai G, Tan H
Received 25 November 2018
Accepted for publication 26 February 2019
Published 10 April 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 2573—2589
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S195934
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Background: In the
past few years, significant progress has been made in inhibiting
neovascularization at the tumor site, cutting off the nutrient supply of the
tumor, and inhibiting tumor growth and metastasis. However, many
proteins/peptides have the disadvantage of poor stability, short half-life, and
uncertain targeting ability. Chemical modification can be used to overcome
these disadvantages; many polyethylene glycol-modified proteins/peptides have
been approved by US FDA. The purpose of this study was to obtain a novel
anti-angiogenic chondroitin sulfate (CS)-peptide nanoparticle conjugate with
efficient anti-neovascularization and tumor targeting ability and an acceptable
half-life.
Materials and methods: The
CS-ES2-AF nanoparticle conjugate was synthesized and characterized using
1H-nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, transmission electron microscopy,
and particle size and zeta potential analyzer. The anti-angiogenic ability was
studied using MTT, migration, tube formation, and chick chorioallantoic
membrane assays. The targeting ability of CS-ES2-AF was studied by ELISA,
surface plasmon resonance, and bioimaging. The pharmacokinetics was also
studied.
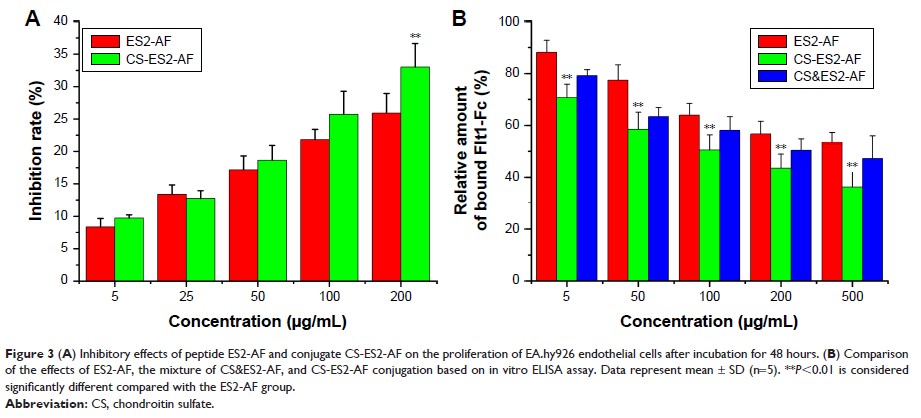
Results: The
CS-ES2-AF could self-assemble into stable nanoparticles in aqueous solution,
which significantly enhances its anti-neovascularization activity, tumor
targeting more explicit, and prolongs its half-life.
Conclusion: CS is an
effective protein/peptide modifier, and CS-ES2-AF displayed good potential in
tumor targeting therapy.
Keywords: chondroitin
sulfate, ES2-AF, nanoparticles, anti-angiogenesis, targeting