110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

前列腺癌前列腺外扩展的表观弥散系数:系统回顾和诊断汇总分析
Authors Bai K, Sun Y, Li W, Zhang L
Received 22 October 2018
Accepted for publication 7 March 2019
Published 11 April 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 3125—3137
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S191738
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Rituraj Purohit
Objective: To
evaluate the diagnostic performance of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) for
local staging of prostate cancer.
Methods: Databases
of Web of Science, MEDLINE (Ovid and PubMed), Cochrane Library, EMBASE, and
Google Scholar were searched up to May 31, 2018, with language restricted to
English. All studies concerning multiparametric magnet resonance imaging
(mpMRI) with ADC for detection of extracapsular extension (ECE, T3a) and/or
extraprostatic extension (EPE, overall stage of T3) were identified by two
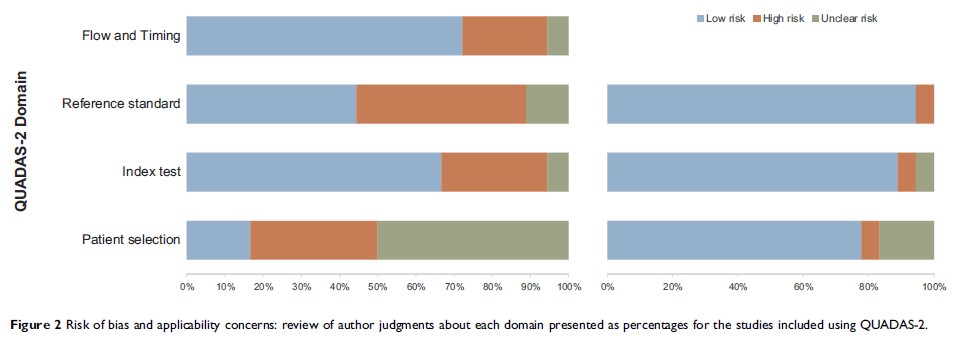
reviewers independently, and quality of included studies was evaluated using
Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies-2 tool. True positive, false
positive, false negative and true negative of each study were extracted to
reconstruct the 2×2 tables for evaluating diagnostic accuracy. Summary
estimates of sensitivity, specificity, and corresponding 95% CIs were
calculated with bivariate model and hierarchical summary receiver operating
characteristic model, then presented in forest plots. Multiple subgroup
analyses and meta-regression were performed, and publication bias was evaluated
with Deeks funnel.
Results: A total
of 18 studies were included, with 6 involved ECE and 12 for EPE. Pooled
sensitivity was 80.5% (95% CI 76.5–83.9%) with specificity of 69.1% (95% CI
62.3–75.2%). Multiple subgroup analyses showed that if ADC and length of
capsular contact are regarded as independent predictors, pooled sensitivity was
85% (95% CI 77–90%) and 81.1% (95% CI 76.0–85.3%), with specificity of 70.8%
(95% CI 56.3–82.0%) and 66.6% (95% CI 57.6–74.5%), respectively.
Meta-regression demonstrated that there was no substantially significant
difference in types of coil, magnet field strength (1.5T versus 3.0T), and
analysis method (per-lesion versus per-patient).
Conclusion: By
introducing ADC to MRI, we could obtain favorable sensitivity for diagnostic
performance of EPE, but with a little decreased specificity.
Keywords: apparent
diffusion coefficient, prostatic cancer, magnetic resonance imaging,
extraprostatic extension, length of capsular contact