110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

左乙拉西坦用于难治性癫痫患者随机安慰剂对照试验的荟萃分析
Authors Chen D, Bian H, Zhang L
Received 19 September 2018
Accepted for publication 1 March 2019
Published 11 April 2019 Volume 2019:15 Pages 905—917
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S188111
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Jun Chen
Objective: The
objective of this study was to investigate the efficacy and safety profile of
levetiracetam as add-on therapy in patients with refractory epilepsy.
Methods: Web of
Science, MEDLINE (Ovid and PubMed), Cochrane Library, EMBASE, and Google
Scholar were systematically searched to identify potential eligible randomized
controlled trials by two reviewers independently. Pooled estimates of risk
ratios (RRs) for 50%, 75%, and 100% reduction from baseline were calculated
using the fixed-effect model or random-effect model. Quality of included
studies was assessed with the Cochrane Collaboration’s Risk of Bias tool.
Serious adverse events and withdrawals induced by interventions and the most
common side effects were analyzed.
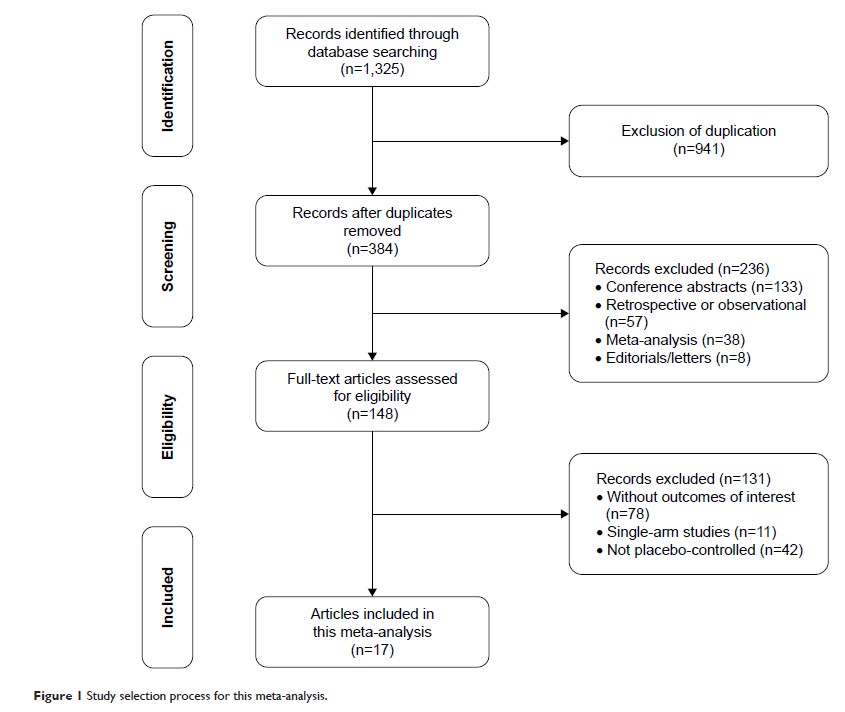
Results: Seventeen
trials with a total of 3,205 participants were included in this meta-analysis,
including 14 trials for adulthood and three trials for children. Pooled
estimates suggested that levetiracetam was an effective anti-epileptic drug at
1,000–3,000 mg/day (RR =2.00 for 1,000 mg/day, RR =2.68 for
2,000 mg/day, RR =2.18 for 3,000 mg/day) for adults and
60 mg/kg/day (RR =2.00) for children compared to placebo in terms of 50%
reduction from baseline. Likewise, as for seizure freedom rate, levetiracetam
had an advantage over placebo at 1,000–3,000 mg/day (RR =5.84 for
1,000 mg/day, RR =4.55 for 2,000 mg/day, RR =4.57 for
3,000 mg/day, respectively) for adults and 60 mg/kg/day (RR =4.52)
for children. Regarding safety profile, patients treated with levetiracetam had
significantly higher occurrence than placebo for somnolence, asthenia,
dizziness, infection, nasopharyngitis, anxiety, and irritability; however, most
studies reported that these adverse events were mild and transient.
Conclusion: Levetiracetam
is an effective anti-epileptic drug for both adults and children with
generalized or partial-onset refractory seizures at 1,000–3,000 or
60 mg/kg/day, with a favorable adverse event profile.
Keywords: levetiracetam,
adjunctive, refractory epilepsy, placebo