110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

MicroRNA-665 通过直接靶向高迁移率族蛋白 B1 并灭活 Wnt/β-连环蛋白途径来抑制视网膜母细胞瘤的致癌性
Authors Wang S, Du S, Lv Y, Zhang F, Wang W
Received 6 January 2019
Accepted for publication 25 February 2019
Published 11 April 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 3111—3123
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S200566
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Chien-Feng Li
Purpose: Previous
studies have revealed that microRNA-665 (miR-665) is dysregulated in a variety
of human cancers. However, little is known regarding its expression profiles
and functions in retinoblastoma (RB). Therefore, the aims of our study were to
evaluate miR-665 expression in RB and determine the precise roles of miR-665 in
the progression of RB.
Patients and methods: Herein,
RT-qPCR was used to determine miR-665 expression levels in RB tissues and cell
lines, and a series of functional experiments were performed to explore the
influence of miR-665 on RB cell proliferation, colony formation, apoptosis,
migration, and invasion as well as tumor growth. The molecular mechanisms
underlying the tumor-suppressive action of miR-665 in RB were also explored.
Results: We found
that miR-665 was markedly reduced in RB tissues and cell lines and that lower
miR-665 expression was strongly associated with tumor size, TNM stage, and
differentiation in patients with RB. Exogenous expression of miR-665 suppressed
cell proliferation, colony formation, migration, and invasion, and induced cell
apoptosis in RB cells, while silencing miR-665 expression had the opposite
effects. In addition, upregulation of miR-665 decreased the tumor growth of RB
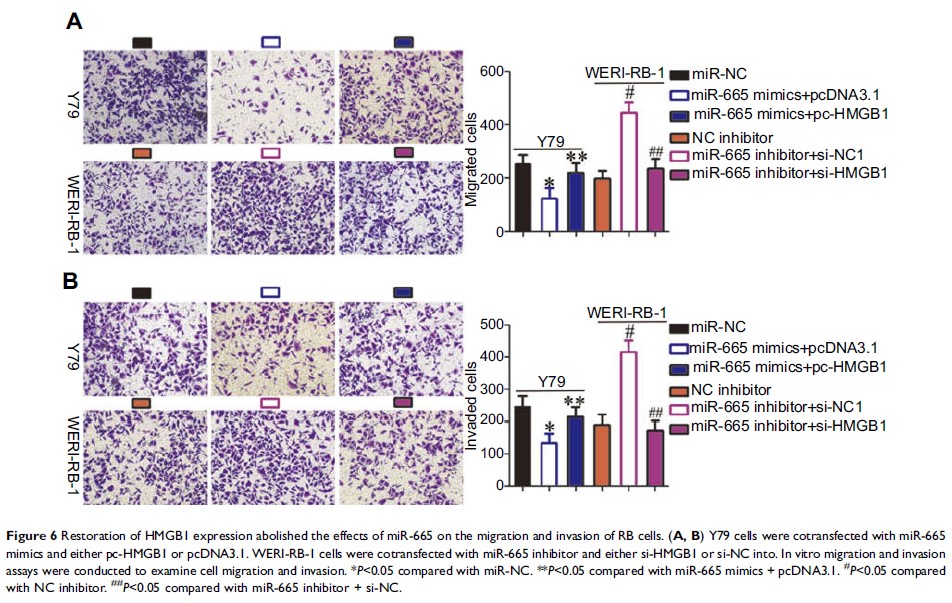
cells in vivo. High-mobility group box 1 (HMGB1 ) was identified as a direct target of miR-665 in
RB cells, and decreasing the expression of HMGB1 simulated
the regulatory effects of miR-665 overexpression in RB cells, while knockdown
of HMGB1 expression
counteracted the miR-665-mediated antitumor effects in RB cells. Moreover,
miR-665 was shown to regulate the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway by
targeting HMGB1 in
vitro and in vivo.
Conclusion: Taken
together, our in vitro and in vivo results suggest that miR-665 acts as a
tumor-suppressive miRNA in RB by directly targeting HMGB1 and
inactivating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Hence, this miRNA is a candidate
prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target in patients with RB.
Keywords: microRNA-665,
retinoblastoma, high-mobility group box 1, Wnt/β-catenin pathway, oncogenicity